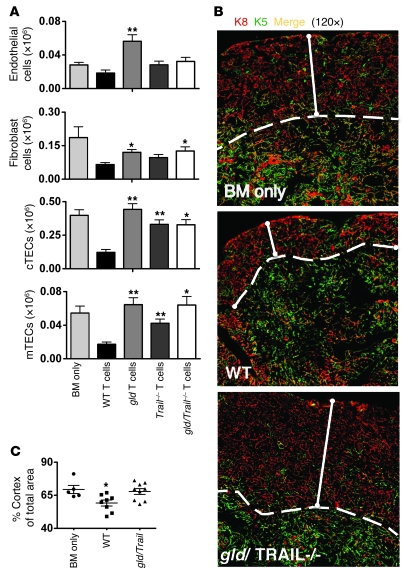
Figure 5. tGVHD causes damage to the thymic stroma, loss of thymic epithelial cells, and cortical thinning.
(A) CD45– thymic stromal cell subsets were assessed by flow cytometry in allo-BMT recipients of TCD-BM with or without WT, Trail–/–, gld, or gld/Trail–/– T cells. Absolute numbers are displayed (mean ± SEM). TCD-BM–only group, n = 9; WT T cells, n = 11; gld T cells, n = 10; Trail–/– T cells, n = 12; gld/Trail–/– T cells, n = 5. Combined data from 2 identical experiments. Endothelial cells, CD45–CD31+MHC class IIdim; fibroblasts, CD45–PDGFR1+MHC class IIneg; cTECs, CD45–CD31–MHC class IIint/hiUEA-1–; mTECs, CD45–CD31–MHC class IIint/hiUEA-1+. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 versus WT T cells. (B) Representative paraffin-fixed thymus sections from the groups that received TCD-BM with or without 0.25 × 106 WT, Trail–/–, gld, or gld/Trail–/– T cells were stained for K8–positive (red) cortical and K5–positive (green) medullary regions and analyzed by confocal microscopy at day 28 after transplant. Dotted lines indicate the corticomedullary junction. Solid lines indicate cortical thickness. Original magnification, ×120. Representative images are shown (n = 2–3/group). (C) Experiment was performed as in B. Three paraffin-fixed thymus sections per thymus, spaced 50 μm apart in each organ, were stained with K5 and K8 antibody and analyzed by confocal microscopy to quantitatively analyze total, medullary, and cortical areas. Averaged percent cortical area (mean ± SEM) was then determined as a fraction of total area. Symbols indicate individual animals. BM-only group, n = 5; WT and gld/Trail–/– groups; n = 8–9; combined data from 2 identical experiments. *P < 0.05 versus BM only.