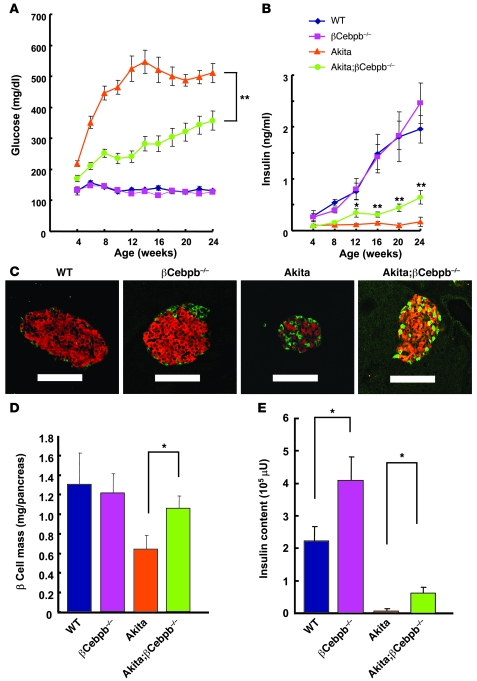
Figure 3. Effects of β cell–specific ablation of C/EBPβ in Akita mice.
(A and B) Blood glucose (A) and plasma insulin (B) concentrations in WT (n = 7), βCebpb–/– (n = 9), Akita (n = 7), and Akita;βCebpb–/– (n = 14) mice in the fed state and at the indicated ages. Data are mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, Akita;βCebpb–/– versus Akita. (C) Pancreatic sections from 8-week-old WT, βCebpb–/–, Akita, and Akita;βCebpb–/– mice were stained with antibodies to insulin (red) and to glucagon (green). Scale bars: 100 μm. (D) Quantitation of β cell mass in 8-week-old WT, βCebpb–/–, Akita, and Akita;βCebpb–/– mice. Data are mean ± SEM from 5 mice per genotype. *P < 0.05. (E) Insulin content of the pancreas of WT, βCebpb–/–, Akita, and Akita;βCebpb–/– mice at 12 weeks of age. Data are mean ± SEM from 4 mice per genotype. *P < 0.05.