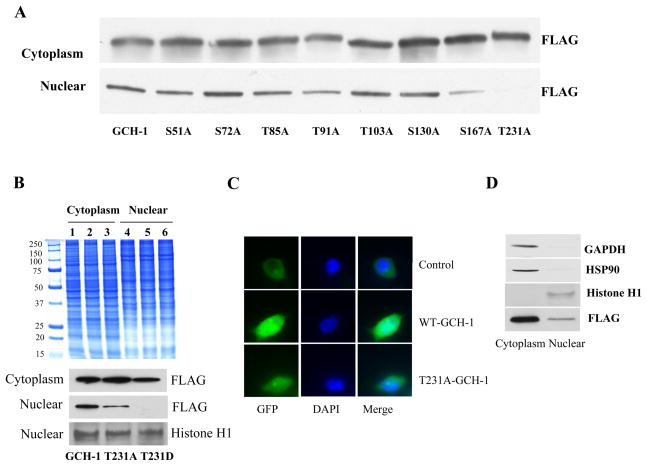
Figure 5.
The effects of GCH-1 phosphorylation mutation on GCH-1 nuclear translocation. (A) Western blot analysis of FLAG expression in cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions from GCH-1 or its mutant’s cells. (B) Coomassie staining of cytoplasmic and nuclear proteins from cells expressing WT-GCH-1, T231A- and T231D-GCH-1 (upper panel); Western blot analysis of FLAG expression in cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions from cells expressing WT-GCH-1, T231A- and T231D-GCH-1. Nuclear fractions were also probed for nuclear marker Histone H1 to assure equal loading of proteins (lower panel). (C) Nuclear localization of GCH-1 and T231A by immunofluorescence staining. HEK293 cells were overexpressed with vector-GFP, GCH-GFP and T231A-GFP and stained with DAPI. (D) Equal amount of cytosolic and nuclear proteins from WT-GCH-1 cells with tetracycline stimulation were run on a SDS/PAGE and probed for GAPDH, HSP90, Histone H1 and FLAG by western blot analysis to determine purity of nuclear fraction.