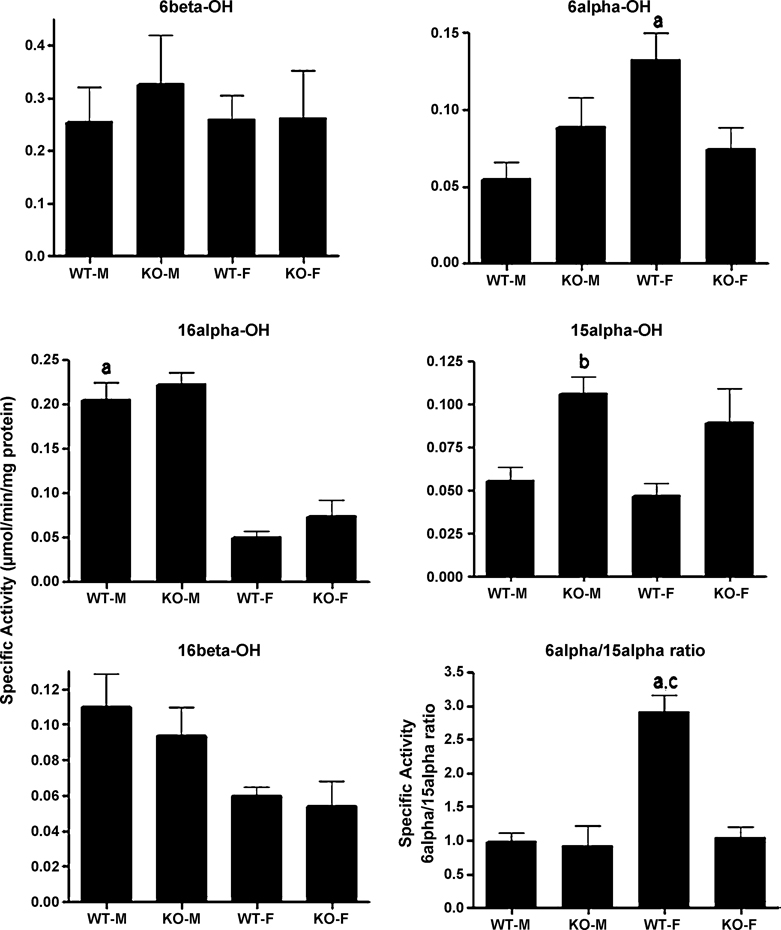
Fig. 1. Gender differences in testosterone hydroxylation in wild-type and CAR-null mice.
Testosterone hydroxylation in the 6β-, 16α-, 16β-, and 6α-positions were determined and compared between male and female wild-type and CAR-null mice. The results are shown as mean specific activity (µmol/min/mg protein) ± SD (n = 5–6). An (a) indicates a significant difference between wild-type male (WT-M) and wild-type female (WT-F) mice, a (b) indicates a significant difference between WT-M and CAR-null male (KO-M) mice, and a (c) indicates a significant difference between wild-type female (WT-F) and CAR-null female (KO-F) mice by ANOVA followed by Fisher’s PLSD test as the post-hoc test (p < 0.05).