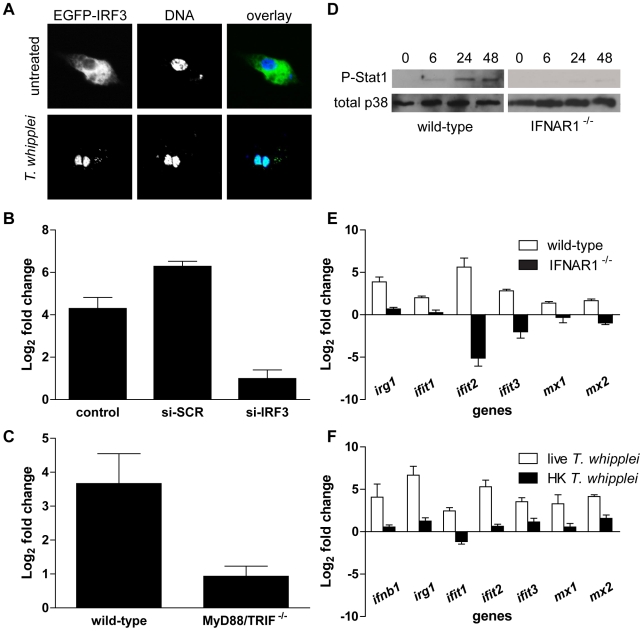
Figure 4. T. whipplei induces a functional type I IFN response.
(A) RAW cells were transiently transfected with IRF3-EGFP before stimulation with T. whipplei (MOI 50∶1) for 4 h. Nuclei were stained with DAPI. (B) RAW cells were transiently transfected with IRF3-specific siRNA (si-IRF3), control scramble siRNA (si-SCR) or left untransfected (control) 24 h before stimulation with T. whipplei (MOI 50∶1). IFN-β expression was monitored after 6 h using qRT-PCR. Results are expressed as the ratio of expression levels in infected cells vs. uninfected cells relative to β actin). (C) BMDM from wild-type and MyD88/TRIF−/− mice were stimulated with T. whipplei (MOI 50∶1) for 6 h and IFN-β expression was monitored using qRT-PCR. Results are expressed as the ratio of expression levels in infected cells vs. uninfected cells relative to β actin). (D) BMDM from wild-type and IFNAR1−/− mice were stimulated for indicated time points with T. whipplei (MOI 50∶1), and lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting. Phospho-STAT1 blots were stripped and reprobed for p38 as loading control. One representative experiment is shown (n = 3). (E) BMDM from wild-type and IFNAR1−/− mice were stimulated with T. whipplei (MOI 50∶1) for 6 h and host responses were monitored using qRT-PCR on indicated genes. Results are expressed as the ratio of expression levels in infected cells vs. uninfected cells relative to β actin). (F) BMDM were stimulated with live and heat-killed T. whipplei (MOI 50∶1) for 6 h and host responses were monitored by qRT-PCR on indicated genes. Results are expressed as the ratio of expression levels in infected cells vs uninfected cells relative to beta actin.