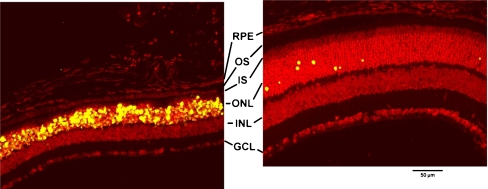
Fig. 9.
Effect of TUDCA on LIRD mouse retina morphology and apoptosis: 15 days post-light exposure. Mice were subcutaneously injected with either vehicle or TUDCA (500 mg/kg), exposed to 10,000 lx of white light for 7 h, then returned to maintenance lighting conditions. Fifteen days after light exposure, mice were killed, and paraffin retina sections were prepared and assayed for fluorescent TUNEL by confocal microscopy. Bright-light-exposure-induced massive apoptosis and morphological damage in retinal photoreceptors of vehicle-treated (left) but not TUDCA-treated eyes (right). Of particular note in the vehicle-treated sample is the thinning of the outer nuclear layer (ONL) and the nearly complete loss of inner segments (IS) and outer segments (OS) of the photoreceptors. Additionally, nearly all the photoreceptor nuclei are TUNEL positive. Conversely, TUDCA-treated samples showed intact photoreceptors, thick ONL, and very few TUNEL-positive photoreceptor cells. Treatment had no discernable effect on the inner nuclear layer (INL), ganglion cell layer (GCL), or retinal pigment epithelium (RPE). Image reprinted with permission from Ref. [81]