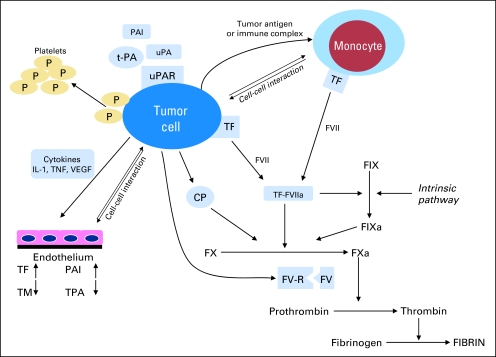
Fig 1.
The tumor cell promotes a hypercoagulable state and activates the hemostatic system, utilizing cell surface proteins such as tissue factor (TF), cancer procoagulant (CP), tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA), urokinase plasminogen activator (uPA), as well as plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 (PAI-1) and 2 (PAI-2). Interaction with other blood cells (eg, monocytes, platelets, endothelial cells) occurs (A) directly by cell-cell interaction; or (B) indirectly by cytokine release promoting prothrombotic endothelial changes. IL, interleukin; P, protein; F, factor; TM, thrombomodulin; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; R, receptor; FV-R, factor V receptor. Adapted from Falanga.5