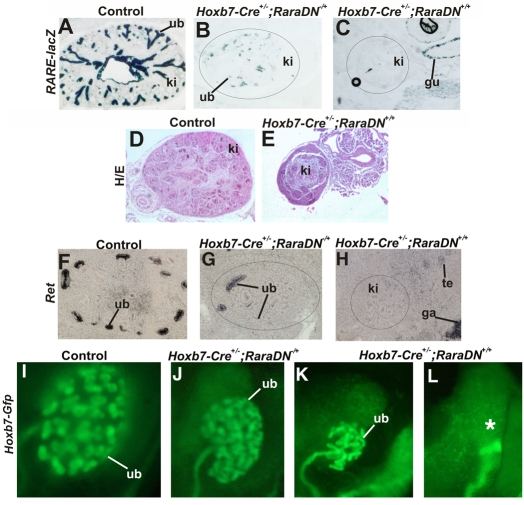
Fig. 5.
Expression of RaraDN in ureteric bud cells inhibits Ret expression and branching in a dose-dependent manner. (A) A lacZ-stained section from a control (Hoxb7-Cre–/–;RaraDNflox/flox;RARE-lacZ) embryo. (B) A lacZ-stained section of an embryo expressing one allele (Hoxb7-Cre–/+;RaraDNflox/+;RARE-lacZ) of the RaraDN transgene. (C) Undetectable lacZ expression in kidneys in an embryo expressing two alleles (Hoxb7-Cre–/+;RaraDNflox/flox;RARE-lacZ) of the RaraDN transgene. (D) A Hematoxylin and Eosin (H/E)-stained section from an E14 Hoxb7-Cre–/–;RaraDNflox/flox control embryonic kidney. (E) An H/E-stained section through a kidney from an Hoxb7-Cre–/+;RaraDNflox/flox embryo. (F) In situ hybridization analysis of a control (Hoxb7-Cre–/–;RaraDNflox/+) embryonic kidney. (G) In situ hybridization analysis of an embryo expressing one allele (Hoxb7-Cre–/+;RaraDNflox/+) of the RaraDN transgene. (H) Undetectable Ret expression in a sectioned kidney from an E14 (Hoxb7-Cre–/+;RaraDNflox/flox embryo) expressing two alleles of the RaraDN transgene. (I) Hoxb7-Gfp expression in a control (Hoxb7-Cre–/–;RaraDNflox/flox) E14 embryonic kidney (J) Reduced branching morphogenesis in a Hoxb7-Cre–/+;RaraDNflox/+;Hoxb7-Gfp E14 kidney from an embryo expressing one allele of the dominant-negative transgene. (K,L) Renal hypoplasia and renal agenesis, respectively, in Hoxb7-Cre–/+;RaraDNflox/flox;Hoxb7-Gfp E14 embryonic kidneys from animals expressing two alleles of dominant-negative RaraDN transgene. The asterisk in (L) denotes renal agenesis. gu, gut; ki, kidney; te, testes; ub, ureteric bud. Magnification: 10× in A-L.