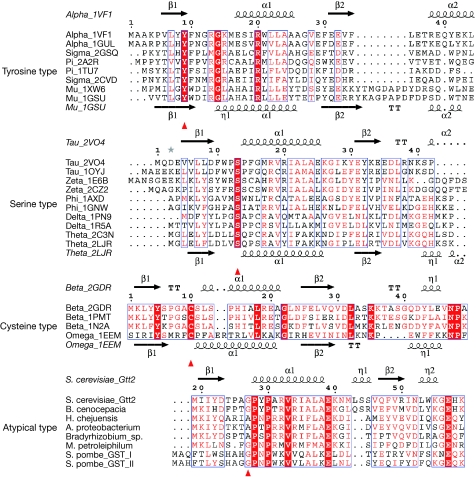
Figure 3.
Conservation of the amino-terminal regions of various types of GST. Sequences of tyrosine, serine and cysteine types are from Protein Data Bank (www.rcsb.org; PDB codes 1TU7, 2A2R, 1XW6, 1GSU, 2CVD, 2GSQ, 1VF1, 1GUL, 2VO4, 1OYJ, 1AXD, 1GNW, 1PN9, 1R5A, 2C3N, 2LJR, 1E6B, 2CZ2, 2GDR, 1N2A, 1PMT and 1EEM). Sequences of the atypical type are downloaded from the National Center for Biotechnology Information database (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov). Codes in parentheses are NCBI accession numbers: Saccharomyces cerevisiae Gtt2, Schizosaccharomyces pombe GST I (Q9Y7Q2), S. pombe GST II (O59827), Burkholderia cenocepacia PC184 GST (YP_002095143), Hahella chejuensis KCTC 2396 GST (YP_437484), Methylibium petroleiphilum PM1 GST (YP_001020104), Alpha proteobacterium HTCC2255 GST (ZP_01450455) and Bradyrhizobium sp. ORS278 GST (YP_001202246). GTS, glutathione sulphonate.