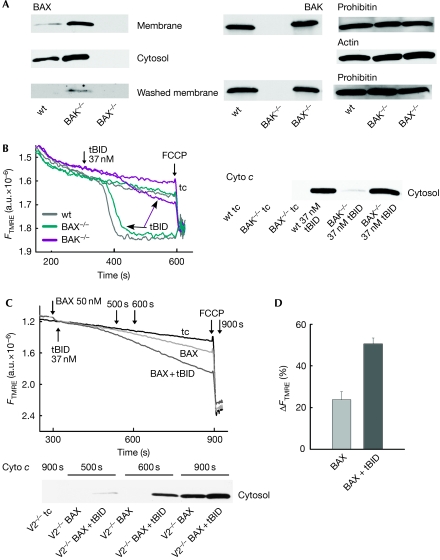
Figure 4.
BAX-dependent tBID-induced ΔΨm loss and cyto c release in permeabilized BAK−/− and V2−/− MEFs. (A) Immunoblot showing the presence of BAX in membrane and cytosol (upper left panels) and BAK in membrane (upper right panel) of permeabilized wt, BAK−/− and BAX−/− MEFs. Membranes from the permeabilized, washed cells were immunoblotted for BAX and BAK (lower two panels). (B) ΔΨm was monitored for permeabilized and washed wt, BAK−/− and BAX−/− MEFs treated with 37 nM recombinant tBID. Immunoblot of rapidly separated supernatants (cytosol) showed the release of cyto c. (C) ΔΨm was monitored for permeabilized V2−/− MEFs treated either with 50 nM oligomeric BAX only (light grey trace) or with 50 nM BAX+37 nM tBID (dark grey trace). The supernatants (cytosol) were rapidly separated at different time points (indicated by arrows) and immunoblotted for cyto c. (D) Cumulative data showing BAX and BAX+tBID induced depolarization of V2−/− MEFs. Cyto c, cytochrome c; FCCP, carbonylcyanide-4-(trifluoromethoxy)-phenylhydrazone; MEF, mouse embryonic fibroblast; tBID, truncated BID; V2−/−, VDAC2−/−; wt, wild type.