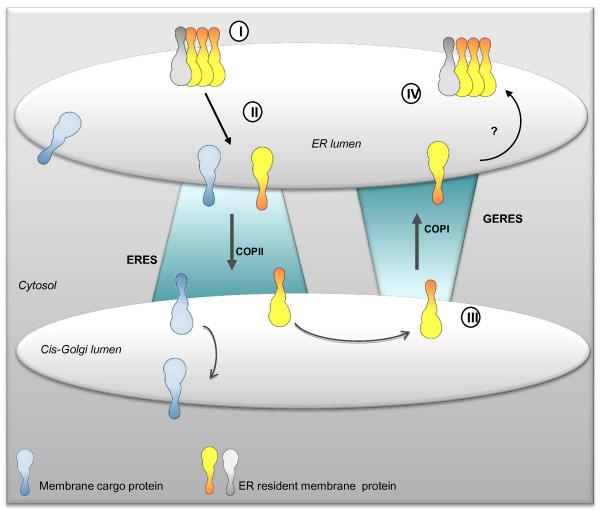
Figure 10.
Schematic representation of mechanisms involved in the location of type II membrane protein in the plant ER. Two mechanisms for ER localization of GCSI are proposed, one being complementary of the other. First, AtGCSI resides in ER subdomains where it forms homo or hetero-oligomers with an unknown partner and is excluded from the ER export sites (ERES) (I). When AtGCSI molecules escape these complexes, they move to the ERES (II) and are transported from the ER to the Golgi in a COPII dependent manner. Once in the Golgi, the COPI machinery would recognize AtGCSI's cytosolic tail (III). Retrograde transport would then occur at Golgi-ER export sites (GERES) to target AtGCSI back to the ER where it would form new complexes with its partners (IV).