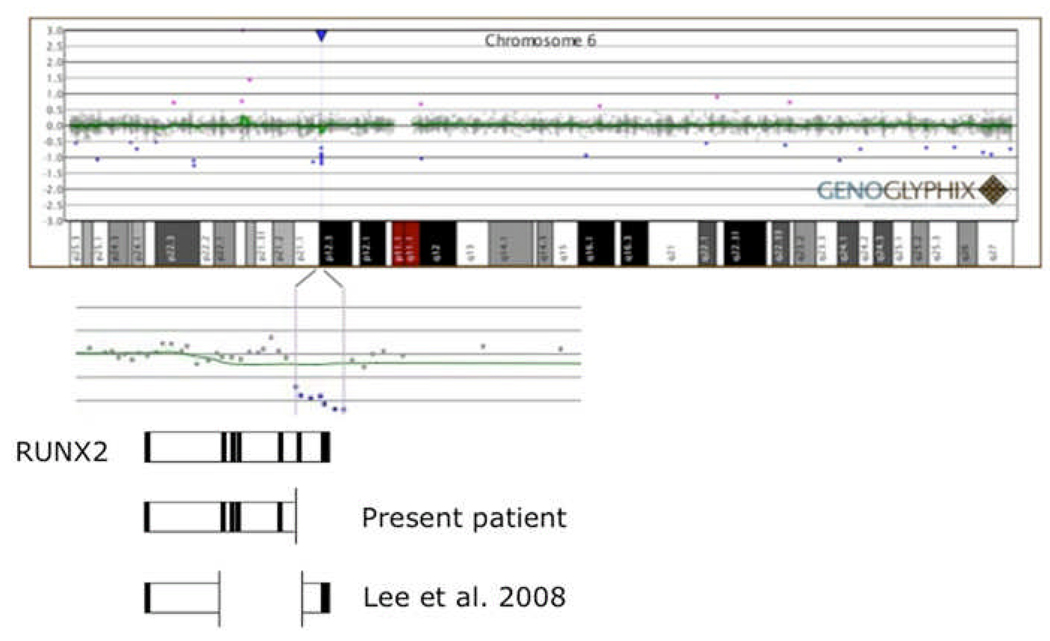
Figure 4.
Disruption of RUNX2 by genomic deletion. An array comparative genomic hybridization (aCGH) plot (Genoglyphix; courtesy Signature Genomic Laboratories) is presented at the top of the figure, above a chromosome 6 ideogram. The deletion encompasses 7 oligonucleotide probes at 6p12.3 which are expanded below the ideogram. The expanded view of the deleted region is overlayed on a cartoon representation of the exon/intron structure of the RUNX2 gene, drawn to approximate horizontal scale. The deletion is predicted to disrupt the C-terminal end of the protein (starting with exon 6), which is involved in transactivation/repression, protein-protein interaction, and includes the nuclear matrix-targeting signal (see text for details). This region is essential for integrating TGFB and BMP2 signaling pathways which are important for osteogenesis.