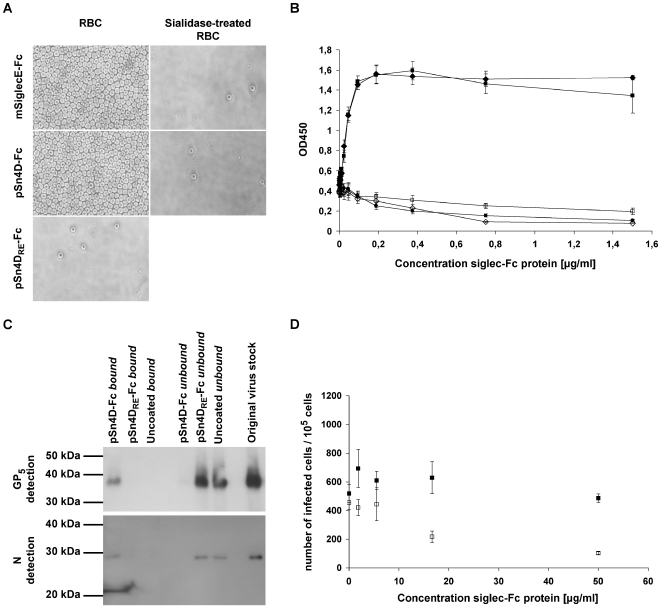
Figure 2. Evaluation of the functionality of pSn4D-Fc as a sialic acid-binding (A & B) and PRRSV-binding (C & D) protein.
Qualitative (A) and quantitative (B) analysis of sialic acid-binding activity using a solid phase red blood cell binding assay. ELISA plates were coated with dilution series of pSn4D-Fc, pSn4DRE-Fc or mSiglecE-Fc protein, after which human RBCs were added and RBC binding was evaluated. pSn4D-Fc + RBCs (black square); pSn4D-Fc + sialidase-treated RBCs (white square); mSiglecE-Fc + RBCs (black diamond); mSiglecE-Fc + sialidase-treated RBCs (white diamond); pSn4DRE-Fc + RBCs (black circle). Values represent means±SEM of 3 experiments. (C) Evaluation of PRRSV-binding activity via immunoprecipitation experiments. Protein A beads were either coated with the pSn4D-Fc or pSn4DRE-Fc protein or not coated and incubated with MARC-145-grown PRRSV at 37°C to allow binding. The bound and unbound fractions were collected and subjected to non-reducing SDS-PAGE and Western Blot analysis using PRRSV N- and GP5-specific mAbs. (D) Evaluation of PRRSV-binding activity via infection-inhibition experiments. A 3-fold dilution series of pSn-Fc protein was mixed with a constant amount of MARC-145-grown PRRSV, incubated for 1 h at 37°C to allow binding and transferred to 105 alveolar macrophages. After 1 h of incubation at 37°C, pSn-Fc - virus mixtures were removed, fresh medium was added to the cells and cells were incubated for 9 h at 37°C, after which they were fixed. Infected cells were then visualized via nucleocapsid-specific immunoperoxidase staining and counted. pSn4D-Fc (white square); pSn4DRE-Fc (black square). Values represent means±SEM of 3 experiments.