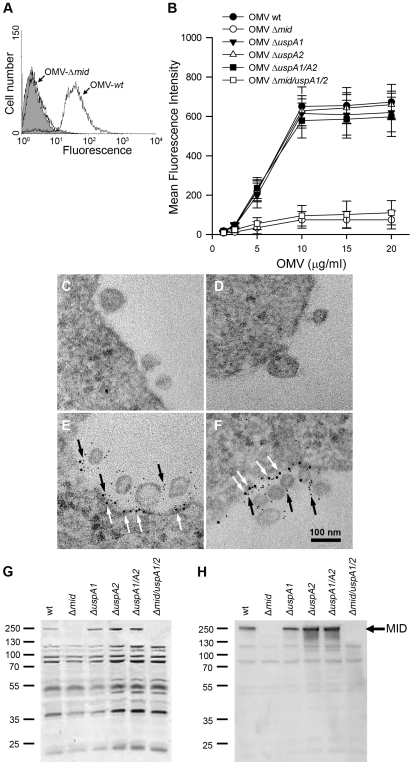
Figure 2. M. catarrhalis OMV bind to tonsillar lymphocytes through an interaction via MID and the IgD B cell receptor.
(A) A typical flow cytometry experiment with OMV and B cells. Control B lymphocytes (shaded) and cells incubated with FITC-labelled OMV wild type (OMV-wt) or MID-deficient OMV (OMV-Δmid). OMV were used at 10 µg/ml and incubated with B cells for 1 h at 37°C. (B) Concentration-dependent binding of OMV to B cells. Increased concentrations of FITC-labeled OMV were incubated with B cells for 1 h followed by flow cytometry analyses. Data are presented as mean±SEM of 3 experiments. (C, D) B cells and OMV interactions analyzed in TEM showed binding of several OMV to the B cell surface. (E, F) IgD molecules were clustered upon OMV binding: gold-labelled antibodies demonstrated formation of a tight cluster of IgD (large granules; white arrows) and MID (small granules; black arrows). The bars represent 100 nm in length. The expression of MID in OMV isolated from different M. catarrhalis isogenic mutants was analyzed by SDS-PAGE (G) and Western blot (H) using MID specific rabbit pAbs. Molecular weight markers in kilodalton are indicated to the left.