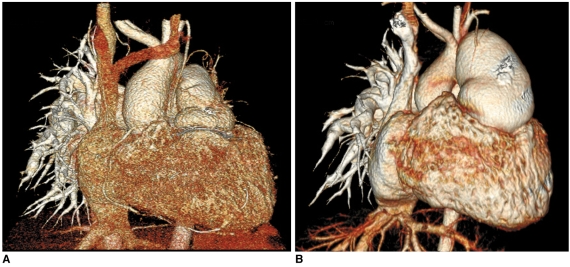
Fig. 2.
Effect of slice thickness on image quality of non-ECG-synchronized spiral CT in 12-year-old boy with pulmonary atresia and ventricular septal defect after Rastelli operation.
A. Volume-rendered CT image reconstructed from thin, overlapped axial images with 0.6-mm slice thickness at collimation of 0.6 mm appears quite grainy. That is because slice thickness is too thin at employed CT dose and this thin slice consequently increases image noise enough to degrade image quality. There are two ways to improve image quality in this situation: one is to slightly increase slice thickness and the other is to increase radiation dose a lot.
B. Slight increase in slice thickness to 0.75 mm substantially improves image quality of volume-rendered CT image. This strategy is highly recommended because its dose saving effect is great.