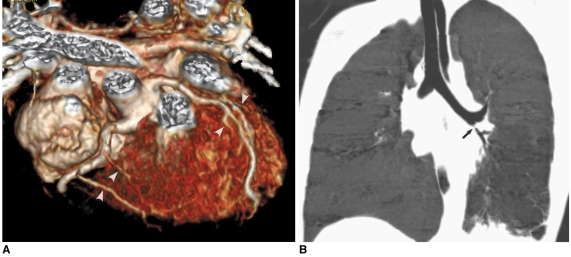
Fig. 7.
Prospective ECG-triggered sequential CT scan in free-breathing young children is relatively less susceptible to respiratory motion artifacts than is retrospectively ECG-gated spiral CT scan. With this scan mode, even side-branches (arrowheads) of coronary arteries (A) and stenosis (arrow) involving left bronchi (B) are clearly delineated without cardiac and respiratory motion artifacts in young children. Therefore, more invasive or sophisticated preparation procedures such as general anesthesia or controlled ventilation are not currently needed for only diagnostic purposes.