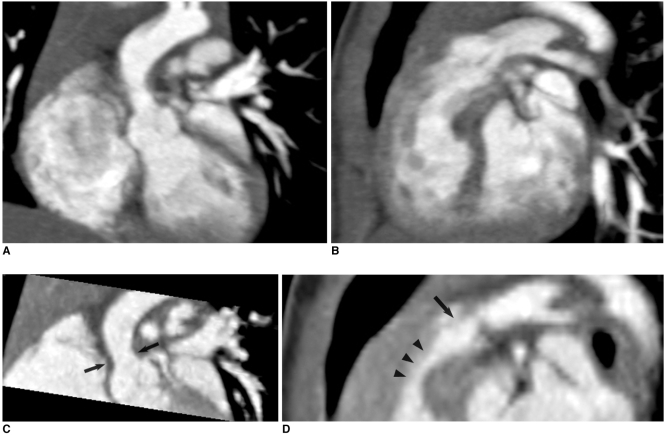
Fig. 9.
Combo CT scan comprised of non-ECG-synchronized spiral scan with usual scan range (A, B) and prospective ECG-triggered sequential scan with narrow scan range confined to conotruncal area of heart (C, D) in 9-months-old boy with Williams syndrome. Supravalvular aortic stenosis (arrows on C) and combined valvar (arrow on D) and subvalvar (arrowheads on D) pulmonary stenoses are clearly shown on prospective ECG-triggered sequential CT images (C, D). Dose estimates are 1.6 mSv for non-ECG-synchronized spiral scan and 0.2 mSv for prospective ECG-triggered sequential scan.