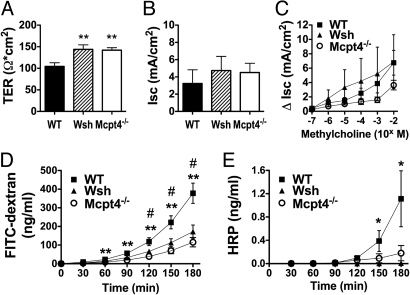
Fig. 1.
Decreased basal intestinal permeability in Wsh and Mcpt4−/− mice. Segments of jejunum from WT, Wsh, and Mcpt4−/− mice were mounted in Ussing chambers and the baseline (A) transepithelial resistance (TER) and (B) short-circuit current (Isc), and (C) β-methylcholine-stimulated changes in Isc were measured. Ex vivo intestinal permeability was measured as luminal-to-serosal flux of (D) FITC-dextran and (E) HRP. Values represent mean± SEM; n = 12–18 mice per group. Statistical significance is: (A) **, P < 0.01 vs. WT; (D) #, P < 0.01 Wsh vs. WT, **, P < 0.01 Mcpt4−/− vs. WT; (E) *, P < 0.05 Wsh vs. WT.