Figure 2. Plk1 is over-expressed in melanoma cells compared to normal melanocytes and Plk1 inhibition causes a decrease in the viability and growth melanoma cells.
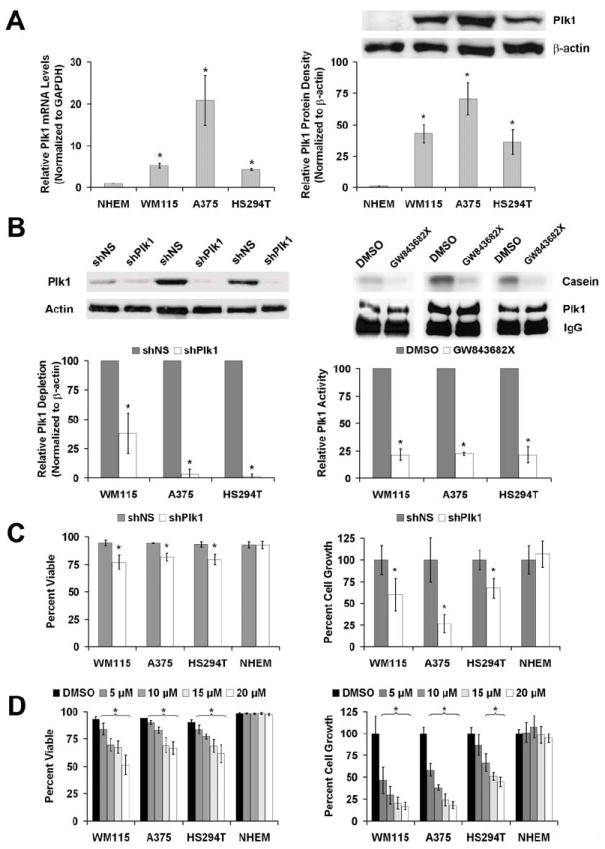
A) Plk1 mRNA and protein levels in melanoma cells versus NHEM. Quantitative real time RT-PCR (left) and Western blot analysis (right) of endogenous Plk1 expression was performed using normal human epidermal melanocytes (NHEM) and three melanoma cell lines WM115, A375 and HS294T. For RT-PCR, Plk1 mRNA levels were quantitated relative to GAPDH mRNA and calculated using the ΔΔCt method. The protein levels were quantitated by a densitometric analysis of protein bands. The data (relative density normalized to β-actin) is expressed as mean ± standard deviation of three experiments (*p<0.01) B) Plk1 inhibition by shRNA and GW843682X. Plk1 protein levels (left) and kinase activity (right) were evaluated following lentiviral transduction via Plk1 shRNA (72 hour) or GW843682X (24 hour) treatments, respectively. Western blot analysis was performed to assess the knockdown of Plk1. Plk1 protein levels were quantitated by a densitometric analysis of protein bands. The data (relative density normalized to β-actin) is expressed as mean ± standard deviation of three experiments (*p<0.01). Kinase activity was measured to assess the inhibition of Plk1 activity. Plk1 was immunoprecipitated from lysates of cells exposed to GW843682X and its ability to phosphorylate casein was evaluated. Phosphorylated casein levels were quantitated and expressed as mean casein phosphorylation relative to the Plk1 protein present in the 10% aliquot of the immunoprecipitation and then normalized to control ± standard deviation of three experiments (*p<0.01). C & D) Effect of Plk1 inhibition on viability and growth of melanoma cells versus NHEM. Following Plk1 shRNA transduction (C) or treatment with GW843682X (D), WM115, A375, HS294T and NHEM cells were counted using Trypan blue analysis (white = viable, blue = non-viable). Cell viability (left panels) was quantitated as percent viable of total cells counted. Cell growth was determined by counting the total number of cells and is quantitated by normalizing each treatment to their respective controls. The data represents mean ± standard deviation of three experiments with similar results (*p<0.01).
