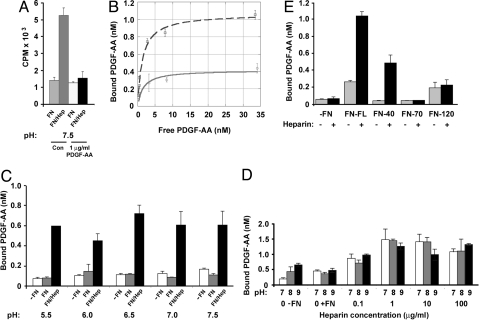
Fig. 1.
PDGF-AA binding to fibronectin is increased by pretreatment of the fibronectin with heparin. (A) Binding of 125I-PDGF-AA, in the presence or absence of excess (1 μg/mL) PDGF-AA, to 40 nM fibronectin was tested at pH 7.5, without (FN) or with (FN/Hep) pretreatment of the fibronectin with 1 μg/mL heparin. Control (Con) wells included 125I-PDGF-AA in the absence of excess growth factor. (B) Adsorbed fibronectin (40 nM) without (solid line) or with 1 μg/mL heparin pretreatment (dashed line), was incubated with 0.35 nM to 34.5 nM 125I-PDGF-AA and the amount bound determined (y axis). Note PDGF-AA effectively self competes and its binding to fibronectin alone reaches a maximum of 0.42 nM, but heparin pretreatment increased this to 1.07 nM. (C) PDGF-AA binding to fibronectin at pH 5.5–7.5 was examined without or with pretreatment of the fibronectin with 100 μg/mL heparin. Wells contained no fibronectin (-FN; white bars), fibronectin (FN; gray bars), or pretreated fibronectin (FN/Hep; black bars). (D) Binding of 125I-PDGF-AA to fibronectin was examined over an increasing concentration of heparin 0.1–100 μg/mL at pH 7 (white bars), 8 (gray bars), or 9 (black bars). (E) PDGF-AA binding to three fibronectin fragments, 40 kDa, 70 kDa, and 120 kDa, was examined without (−) or with (+) 1 μg/mL heparin pretreatment. Full-length fibronectin (FN-FL) and all fibronectin fragments were used at equimolar concentrations (40 nM). No fibronectin (−FN). Data are representative of at least two independent experiments.