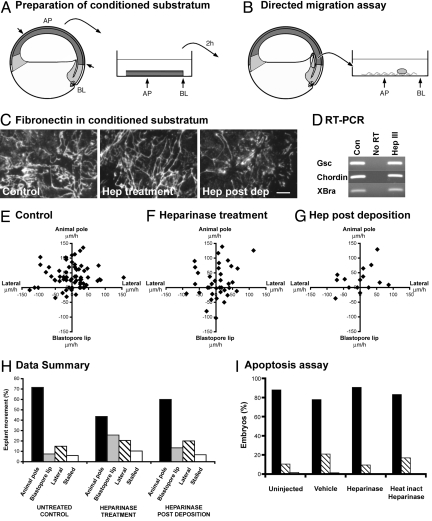
Fig. 2.
Heparinase III treatment disrupts the directed migration of embryonic mesendoderm cells. (A and B) Ex vivo assay for directed cell movement of head mesendoderm cells. (A) Preparation of conditioned substrata. Schematic of a sagital section of a stage 10 Xenopus laevis embryo. The cell sheet (blastocoel roof) that supports the migration of mesendoderm cells in vivo is removed (short arrows indicate dissection) and placed matrix-side down on a tissue culture dish. The position and orientation of the tissue is marked on the dish. After 2 h, the tissue is removed leaving the deposited ECM. (B) Directed Migration Assay. An explant of anterior mesendoderm (circle) is dissected at stage 10.5 and placed on the ECM at the mid point between the blastocoel lip (BL) and animal pole (AP) marks. The explant position is recorded immediately and 1 h later. (C) Following the migration assay, the conditioned substrata are subjected to immunocytochemistry for fibronectin. (D) RT-PCR analysis of anterior mesendoderm explants. (E–G) The position of each mesendoderm explant after 1 h is plotted with all starting positions superimposed on the origin. Positive y values indicate movement toward the animal pole, the normal direction of migration. (E) Control, (F) 0.1 U/mL heparinase III included throughout the experiment. (G) ECM treated with 0.1 U/mL heparinase III for 45 min immediately following its deposition. (H) Bar graph of data in E–G. Direction of movement: animal pole (black bars), blastopore lip (gray bars), lateral (moved <15 μm on the y axis but >15 μm on the x axis; hatched bars), stalled (moved less that 15 μm on both axes; white bars). (I) Graph indicating the absence (black bars) or presence (hatched bars) of apoptotic cells in the blastocoel cavity following microinjection of vehicle, heparinase III, or heat-inactivated heparinase III. Dead embryos (white bars). All experiments were repeated at least three times. [Scale bar, 10 μm (E; applies to frames C–E.)]