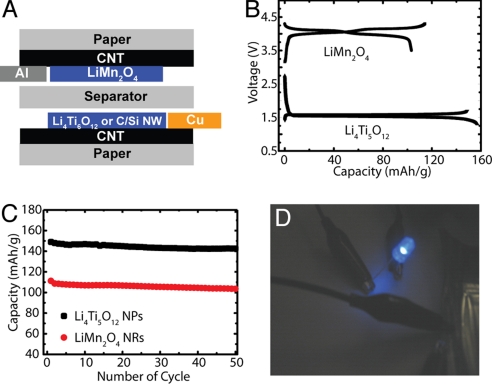
Fig. 4.
Conductive paper as the current collector for Li-ion batteries. (A) Schematic illustration of the conductive paper battery configuration. The metal leads contact only CNTs but not active materials. Lithium foil is used as the counter electrode in half-cell tests. (B) Galvanostatic charging/discharging curves of LiMn2O4 nanorod cathode (3.5–4.3 V) and Li4Ti5O12 nanopowder anode (1.3–1.7 V) half-cells with conductive paper current collectors. The current rate is C/5. (C) Cycling performance of LiMn2O4 nanorod (C/3, 49 mA/g) and Li4Ti5O12 nanopowder (C/3, 58 mA/g) half-cells. (D) A 5 cm2 paper battery (a full cell with LiMn2O4 nanorod cathode, C/Si core/shell NW anode, and conductive paper current collectors) used to repeatedly light up a blue LED.