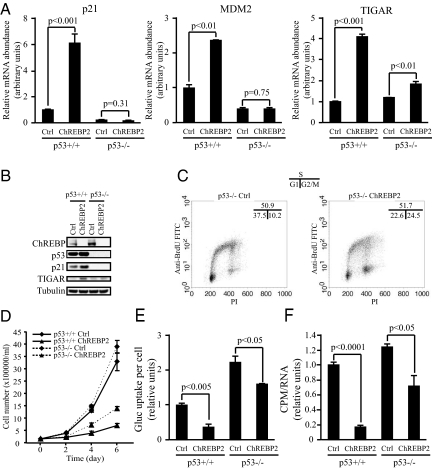
Fig. 4.
p53 is an important mediator of the growth and metabolic phenotype induced by ChREBP suppression. Data in (A) and (D–F) are presented as the mean ± SD of triplicate samples. Data in (B) and (C) are representative of at least three experiments. (A) Quantitative PCR analysis of p21, MDM2 and TIGAR in p53+/+ and p53−/− HCT116 cells transfected with either control or ChREBP2 siRNA at day 3 post-transfection. (B) Western blot analysis of p53+/+ and p53−/− HCT116 cells transfected with either control or ChREBP2 siRNA using indicated antibodies at day 3 post-transfection. (C) FACS analysis for BrdU incorporation and DNA content (PI) of p53+/+ and p53−/− HCT116 cells transfected with either control or ChREBP2 siRNA and pulse labeled with BrdU at day 3 post-transfection. Numbers indicate the percentage of cells in the G1, S, and G2/M phases. (D) Cell proliferation of p53+/+ and p53−/− HCT116 cells transfected with siRNA for control and ChREBP2. (E) Glucose uptake of p53+/+ and p53−/− HCT116 cells transfected with either control or ChREBP2 siRNA at day 3 post-transfection. The data were normalized by cell number. (F) Measurement of RNA synthesis from D-[U-14C6] glucose in p53+/+ and p53−/− HCT116 cells transfected with either control or ChREBP2 siRNA at day 3 post-transfection. The data were normalized by RNA amount.