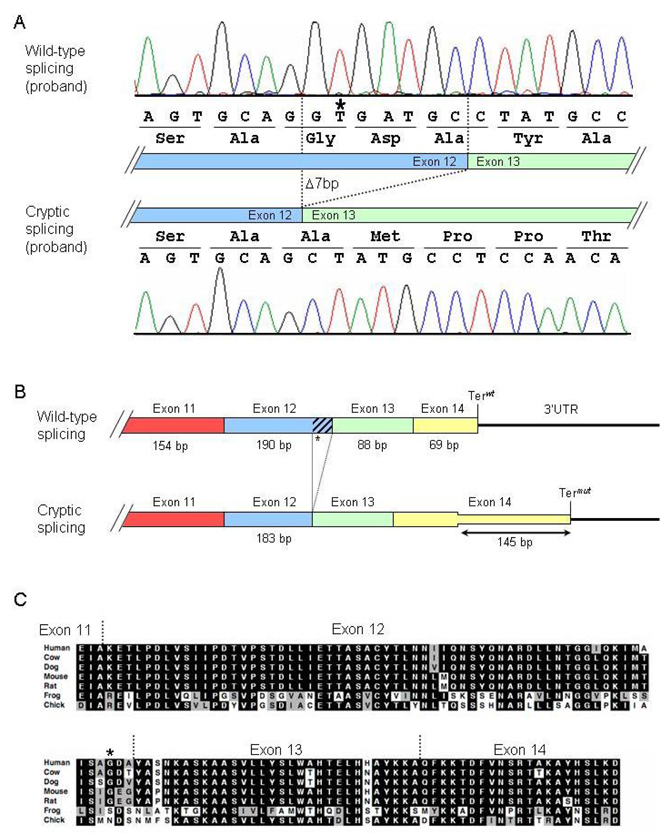
Figure 3.
Cryptic splicing of the PKP2 transcript caused by the 2484C→T mutation. A: Chromatograms of cloned RT-PCR products. Top panel: wild-type splicing in the proband. Bottom panel: mutant splicing results in deletion of the last seven nucleotides in exon 12 and causes a subsequent frame shift. B: Diagram illustrating consequences of cryptic splicing on translation. Exons are indicated by boxes, and the 3’UTR is drawn as a line. Terwt and Termut indicate the wild-type and mutant termination codons, respectively. C: ClustalW sequence alignment of plakophilin-2 orthologs demonstrating conservation of the C-terminal residues that are disrupted in the mutant splice forms. The G828G mutation is indicated with an asterisk (*). Black shading, residue identity; gray shading, conservation of residue character.