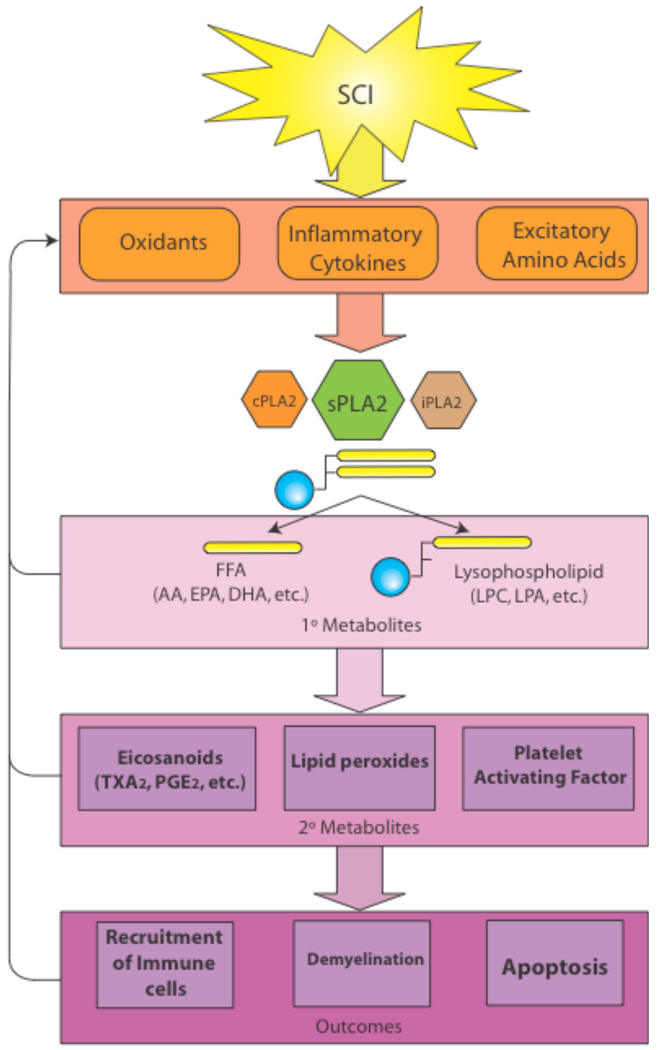
Fig. (3). Overview of sPLA2’s role in spinal cord injury.
The toxicity of sPLA2 is compounded by three factors. 1) sPLA2 is upregulated by commonly known neurotoxic mechanisms such as oxidative stress, cytokines, and EAA. 2) Both the primary metabolites of sPLA2 activity, such as free fatty acids and lysophospholipids, and the secondary metabolites, such as eicosanoids and platelet activating factor, are toxic to the CNS. 3) Finally, sPLA2 has been shown to reciprocally upregulate oxidative stress, cytokines, and EAA thus propagating a positive feedback loop resulting in cytotoxicity and secondary SCI. It must also be noted that sPLA2 does not work in isolation from cPLA2 and iPLA2, rather a reciprocal activity is often demonstrated among the PLA2 subfamilies.