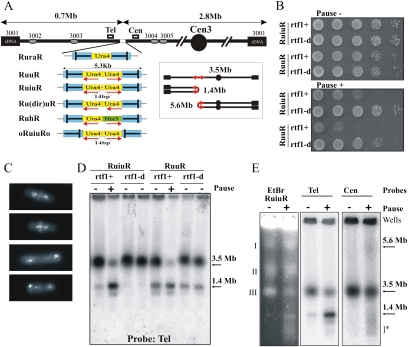
Figure 2.
Replication fork arrest within a palindrome causes the formation of acentric and dicentric chromosomes. (A) Schematic of the constructs integrated at the ura4 locus on ChrIII. (Blue) RTS1; polar RTS1. The bar in RTS1 indicates the direction that, when a fork approaches, it will be arrested. Red arrows below the ura4 (yellow) and his3 (green) sequences indicate the direction of transcription. Boxes Cen and Tel indicate position of probes used. Ovals show the ars sequences. (Inset) Schematic of acentric and dicentric chromosomes. The 14-bp insertion interrupts the symmetry of the palindrome center in RuiuR and oRuiuRo. (B) Viability analysis of perfect (RuuR) and interrupted (RuiuR) palindrome strains in the presence (pause on; +, rtf1+) and absence (pause off; −, rtf1+ or rtf1-d) of fork arrest. Note that loss of viability is dependent on fork arrest by rtf1+ induction. (C) Representative images of RuiuR mitotic catastrophe 24 h after thiamine removal (approximately three generations of growth under conditions in which forks arrest at RTS1). DNA stained with DAPI, and septum stained with Calcofluor. (D) PFGE and Southern blot analysis of strains either unable to arrest forks at RTS1 (rtf1Δ) or where rtf1 is regulated by thiamine ([−] low transcript and minimal arrest; [+] high transcript and efficient fork arrest). Note that formation of 1.4-Mb DNA is correlated with loss of viability in B. (E) PFGE and Southern blot analysis of cells without fork arrest (off; −) and 24 h after (on; +) arrest is induced. (Left panel) Ethidium bromide staining. (Middle panel) Telomere-proximal probe. (Right panel) Centromere-proximal probe. I, II and III indicate fission yeast chromosomes. Arrows: 3.5 Mb, ChrIII; 1.4 Mb, acentric; 5.6 Mb, dicentric. (*) Smear corresponding to breakage.