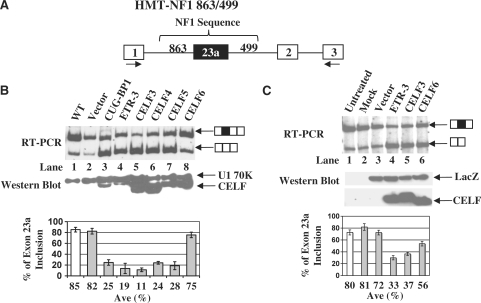
Figure 3.
Over-expression of CELF proteins in HeLa cells promotes exon 23a skipping. (A) Schematic diagram of the HMT-NF1 863/499 reporter construct. (B) Co-transfection of HeLa cells with the HMT-NF1 reporter (2 µg) and CELF protein expression plasmids (1 µg for CUG-BP, ETR-3, CELF4 and CELF5 and 0.5 µg for CELF3 and CELF6). Total RNA was isolated from transfected cells and semi-quantitative RT–PCR was performed using oligonucleotides indicated in panel A. The percentage of NF1 exon 23a inclusion is displayed in the bar graphs. Error bars indicate standard deviations and n = 3. Total protein was isolated from transfected cells and western blot analysis was carried out using Anti-Xpress antibody. Anti-U1 70K antibody was used as a loading control. (C) Co-transfection of HeLa cells with LacZ (4 µg) and CELF protein expression plasmids (4 µg for ETR-3, CELF3 and CELF6). Total RNA was isolated from transfected cells and semi-quantitative RT–PCR, using oligonucleotides that anneal to NF1 exons 23 and 24, was performed to determine the endogenous NF1 exon 23a inclusion. The percentage of NF1 exon 23a inclusion is displayed in the bar graph, with error bars indicating standard deviations. Total protein was isolated from the transfected cells and western blot analysis was performed using Anti-Xpress antibody to detect either tagged CELF proteins or LacZ which was used as a loading control.