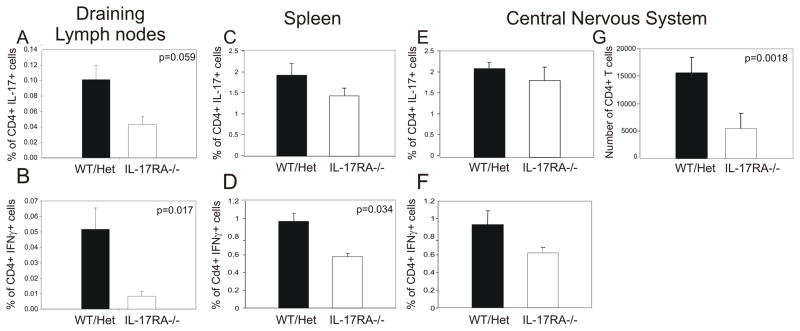
Figure 2.
MOG-specific Th1 responses were reduced in IL-17RA −/− mice. Wild type mice (WT), IL-17RA +/− (Het), and IL-17RA −/− littermates were immunized with MOG35–55 peptide to elicit EAE. At ten days post-immunization, lymphocytes were isolated from draining lymph nodes, spleens, and CNS and stimulated with MOG35–55 peptide as described in Materials and Methods. Frequencies of CD4+ T cells that made IL-17 (A, C, E) or IFNγ (B, D, F) among total lymphocytes were determined by intracellular cytokine staining assay. The number of CD4+ T cells infiltrating CNS (G) was calculated based on flow cytometry and cell count. Six IL-17RA −/− and six wild type and IL-17RA +/− mice were used. Student T test was performed.