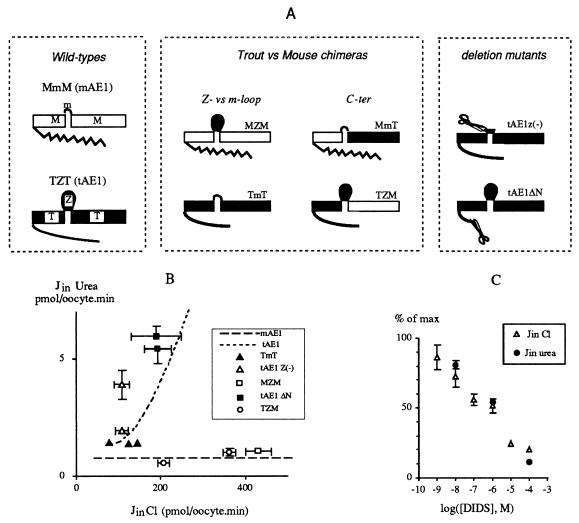
Figure 5.
Permeabilities of chimeras and deletion mutants. (A) Construction of chimeras and deletion mutants. The extracellular loops between transmembrane helices 5 and 6 are termed “Z” and “m” for the trout and mouse exchangers, respectively. The domains of proteins up and down the major extracellular loops are termed “T” and “M” for the trout and mouse, respectively. Thus, wild-type proteins mAE1 and tAE1 are termed “MmM” and “TZT,” respectively. Trout vs. mouse chimeras: MZM, TmT, TZM, MmT (this last chimera, MmT, was not expressed functionally). Deletion mutants: tAE1 z(−) is devoid of amino acids 551–574 located in the extracellular loop between the putative transmembrane helices 5 and 6 of the trout exchanger; tAE1 ΔN is devoid of amino acids 1–311. (B) Correlation between urea permeability and chloride permeability for oocytes expressing several chimeras (TmT, TZM, MZM) or tAE1 mutants [tAE1 Z(−), tAE1 ΔN]. Values are means from eight individual measurements (sometimes error bars are hidden by symbols). The average equivalent relationships established for tAE1 and mAE1 (see Fig. 4A) are indicated by dotted and dashed lines, respectively, the experimental points being omitted for the purpose of clarity. (C) Inhibitory effect of DIDS on both chloride flux and urea transport in TmT-expressing oocytes. (n = 8.)