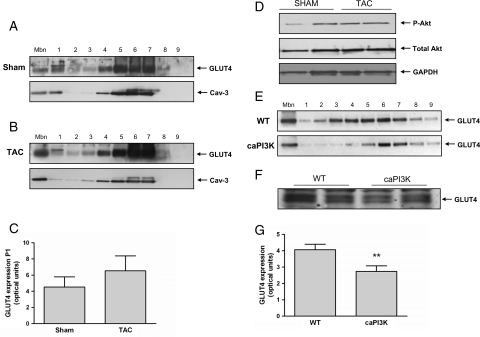
Figure 7.
Glucose transporter 4 in mice with left-ventricular dysfunction or constitutively active phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase (caPI3K). (A) Representative immunoblots of GLUT4 in the sarcolemmal fraction (Mbn), across subcellular fractions (1–9) (upper panel) and of Cav-3 loading control (lower panel) in sham-operated mice. (B) Representative immunoblots of GLUT4 in the sarcolemmal fraction (Mbn), across subcellular fractions (1–9) (upper panel) and of Cav-3 loading control (lower panel) in transverse aortic constriction-induced left-ventricular dysfunction mice. The experiment was repeated three times with similar results. (C) Quantification of GLUT4 levels at the sarcolemma in arbitrary optical units; sham (n = 4) and transverse aortic constriction (n = 4). (D) Representative immunoblots of phospho-Akt, total Akt, and GAPDH (loading control) in transverse aortic constriction vs. controls (n = 3). (E) Representative immunoblots of GLUT4 in the sarcolemmal fraction (Mbn) and across subcellular fractions (1–9) in wild-type (WT, upper panel) and caPI3K (lower panel) mice. (F) Immunublot of GLUT4 levels in total cell lysates from control (WT) and caPI3K mice. (G) Quantification of GLUT4 levels at the sarcolemma in arbitrary optical units; wild-type (n = 3), caPI3K (n = 3), (*P < 0.01).