Fig. 5.
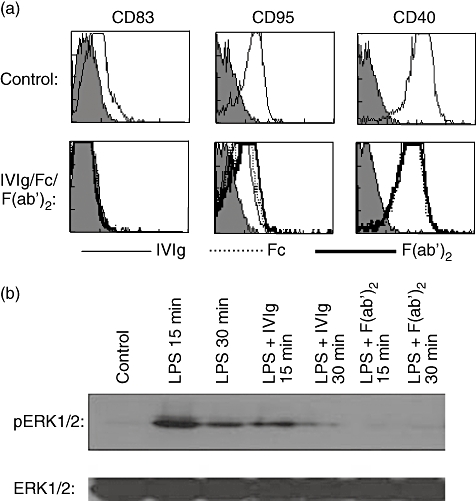
Dendritic cell (DC)-SIGN and α2,6-sialylated immunoglobulin (Ig)G Fc interaction is dispensable for the anti-inflammatory activity of intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIg) on human DCs. (a) Immature monocyte-derived human DCs were incubated in the presence of equimolar concentrations (0·15 mM) of IVIg (thin lines) or F(ab′)2 fragments of IVIg (thick lines) or Fc fragments (dashed lines) for 48 h. The surface markers were analysed by flow cytometry. The upper panel shows DCs cultured in the presence of granulocyte–macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) and interleukin (IL)-4 alone. This research was originally published by Bayry et al. Inhibition of maturation and function of dendritic cells by intravenous immunoglobulin. Blood 2003; 101: 758–765 [21]. © the American Society of Hematology. (b) Immature DCs were cultured in the presence of 0·15 mM IVIg or F(ab′)2 fragments of IVIg for 12 h. The cells were then exposed to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) (1 µg) for 15 and 30 min. The activation of extracellular regulated kinase (ERK)1/2 was monitored by immunoblotting with antibody to phospho-ERK1/2 (pERK1/2). An equal amount of protein loaded in each lane was confirmed with immunoblotting by using antibody to the non-phosphorylated form of ERK1/2 (ERK1/2).
