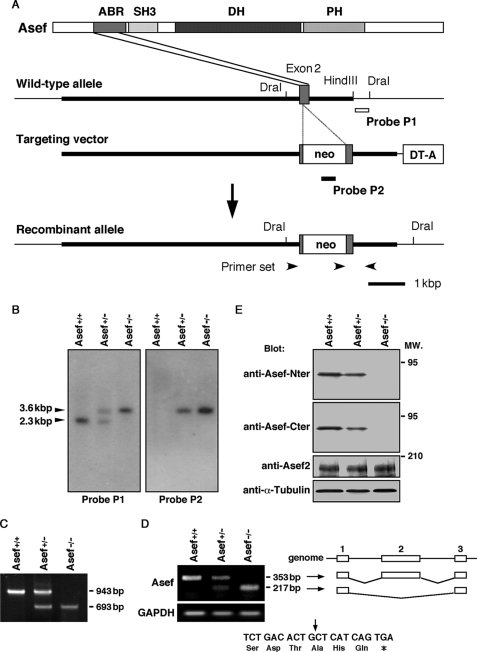
FIGURE 1.
Targeted disruption of the mouse Asef gene. A, construct containing a portion of the wild-type allele, targeting construct, and recombinant locus are shown. Asef was inactivated by the insertion of a neomycin cassette (neo) into codon 73 of Asef. The diphtheria toxin A cassette (DT-A) was placed outside the 3′ homologous region for negative selection. The probe P1 used for detection of homologous recombinants is represented by the open bar, and the probe P2 used for detection of a single insertion of the neomycine gene is represented by the filled bar. The primer set used for detection of recombinants is also represented by black arrowheads. ABR, APC-binding region; PH, Pleckstrin homology domain. B, the mutated Asef locus was identified by Southern blot analysis of genomic DNA digested with DraI and hybridized to internal (Probe P2) and external (Probe P1) genomic fragments. The 2.3-kbp fragment represents the wild-type allele, and the 3.6-kbp fragment represents the homologous recombinant allele. C, shown is a PCR analysis of genomic tail DNA from wild-type (Asef+/+), heterozygous (Asef+/−), and homozygous (Asef−/−) mice with three primers indicated in A. The 943 and 693-bp fragments represent the Asef wild-type and targeted alleles, respectively. D, analysis of Asef mRNA expression is shown. Reverse transcription-PCR analysis was performed on total RNA isolated from brains of Asef+/+, Asef+/−, and Asef−/− mice using primers located in exons 1 and 3. The 353-bp fragment represents the full-length transcript, whereas the 217-bp fragment lacks exon 2. Schematic representation of the structures of the 353- and 217-bp fragments are shown in the right panel. Lines indicate introns, and boxes indicate exons. The 217-bp fragment is derived from the direct splicing of exons 1–3, which introduces a stop codon 3 amino acids downstream in exon 3 and generates a truncated peptide of 104 amino acids (bottom; the arrow indicates the out-of-frame junction). Expression of GAPDH was examined as an internal control. E, an immunoblotting analysis of mutant mice is shown. Lysates prepared from the brain of adult Asef+/+, Asef+/−, and Asef−/− mice were analyzed by immunoblotting with antibodies against the amino-terminal (Nter) or carboxy-terminal (Cter) regions of Asef or Asef2. Anti-α-tubulin antibody was used as a control. MW., molecular weight.