FIGURE 10.
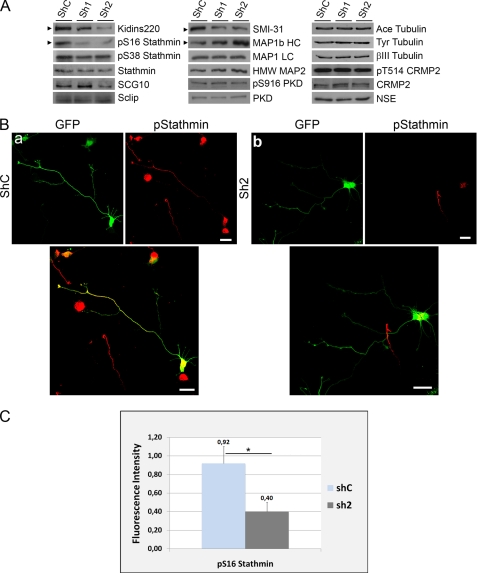
Kidins220/ARMS knockdown modulates the phosphorylation of stathmins and MAP1b-HC. A, hippocampal neurons were transfected with control (shC) or Kidins220/ARMS-specific (sh1 and sh2) shRNA vectors, and Kidins220/ARMS protein levels were determined after 4 DIV by immunoblot analysis. The same lysates were probed for phosphorylated forms of stathmin (Ser(P)-16 (pS16) and Ser(P)-38 (pS38)); total stathmin, SCG10, and Sclip; the phosphorylated form of MAP1b (SMI-31 antibody, 320–340 kDa band); total MAP1b HC and LCs; MAP2; Ser(P)-916 (pS916) PKD; and total PKD as well as for the acetylated and tyrosinated forms of α-tubulin, βIII tubulin, Thr(P)-514 (pT514) CRMP2, and total CRMP2. Neuronal specific enolase (NSE) is shown as a control. The arrowheads indicate immunoblots for which significant signal intensity changes were observed. One representative immunoblot of three independent experiments is shown. B, hippocampal neurons were transfected with GFP-shC (a) as control or GFP-sh2 Kidins220/ARMS-specific shRNA (b) and immunostained with antibodies against Ser(P)-16-stathmin (red). GFP signal served to identify neurons transfected with the different shRNAs. Scale bar, 20 μm. C, quantification of the relative fluorescence intensity for Ser(P)-16-stathmin on GFP-positive (transfected) neurons with respect to GFP-negative (untransfected) cells. Although shC-transfected neurons display a nearly identical intensity of Ser(P)-16-stathmin as untransfected neurons (ratio is almost 1), Ser(P)-16-stathmin decreases significantly in sh2-transfected neurons. The data shown are the means ± S.E. of three independent experiments (shC n = 52 cells, sh2 n = 74 cells), and statistical significance was evaluated by Student's unpaired t test (*, p < 0.05).