FIGURE 7.
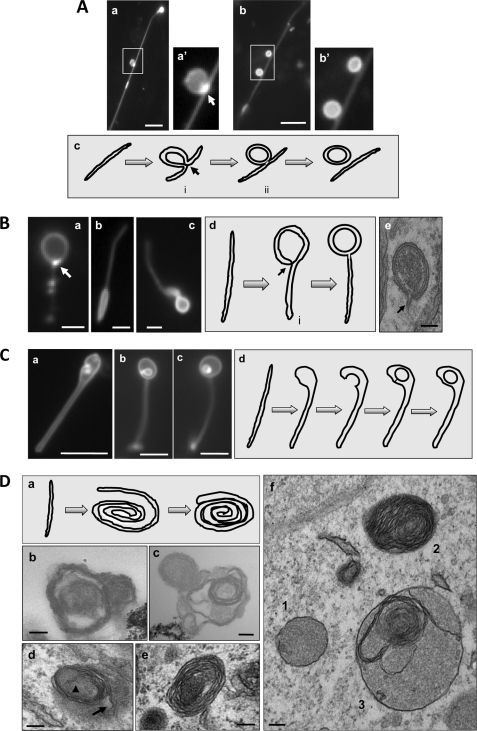
Topological configurations of LC3-TVS, groups II–V. A, group II. HEK-293-GFP-LC3 cells treated with CPP for 3 h were lysed. Two representative LC3-TVS that seemed to be topologically related (panels a and b) were presented. Boxed area in panels a and b are enlarged in panels a′ and b′, respectively. Panel a is the same as Fig. 2C, panel d. It is represented here to demonstrate the vesicle-tubule relationship. Panel c suggests a possible topological derivation of a vesicle from a tubular membrane with the intermediates i and ii resembling those shown in panels a and b, respectively. The arrow in panels a′ and c indicates the possible fusion site where the GFP-LC3 signal was particularly concentrated. Scale bar, 5 μm. B, group III. LC3-TVS identified in HEK-293 (panels a and c) or HCT-116 cells (panel b) treated with EBSS (panels a and b) or CPP (panel c) are presented to suggest a topological origin from a tubular membrane as illustrated in panel d. The intermediate vesicle (denoted with i in panel d) could be identified in EM (panel e and Fig. 3, panel d). The arrows in panels a and d indicate the possible fusion site where the GFP-LC3 signal was particularly concentrated. Panel e demonstrates a double-membrane autophagosome, which was identified in an intact HEK-293 cell treated with CPP. Note the tubular stem extending from the double-membrane vesicle (arrow). Scale bars, 1 μm (panels a and b), 2 μm (panel c), and 100 nm (panel e). C, group IV. Three LC3-TVS (panels a–c) from HEK-293-GFP-LC3 cells treated with CPP are presented, and their topological relationship could be as is illustrated in panel d, in which the tubule expands at one end, which is followed by invagination and internal vesicle formation. Scale bar, 5 μm. D, group V. Panel a shows a schematic representation of the formation of the roll-like vesicles. The tubular membrane may roll around the substrates to form a loose bundle, which may then be compacted and delimited by the outermost layer of the membrane. Electron microscopic examination of HEK-293-GFP-LC3 cells treated with CPP (panels d–f) or the LC3-TVS isolated from these cells (panels b and c) demonstrated the presence of multiple-membrane vesicles, which could be derived from the membrane rolling as illustrated in panel a. The arrowhead and arrow in panel d indicate the proximal and distal ends of the rolling tubule, respectively. Panel f also shows a vesicle (vesicle 3) with the combined morphology of vesicle 1 (double-membrane) and vesicle 2 (multimembrane). Scale bar, 100 nm.