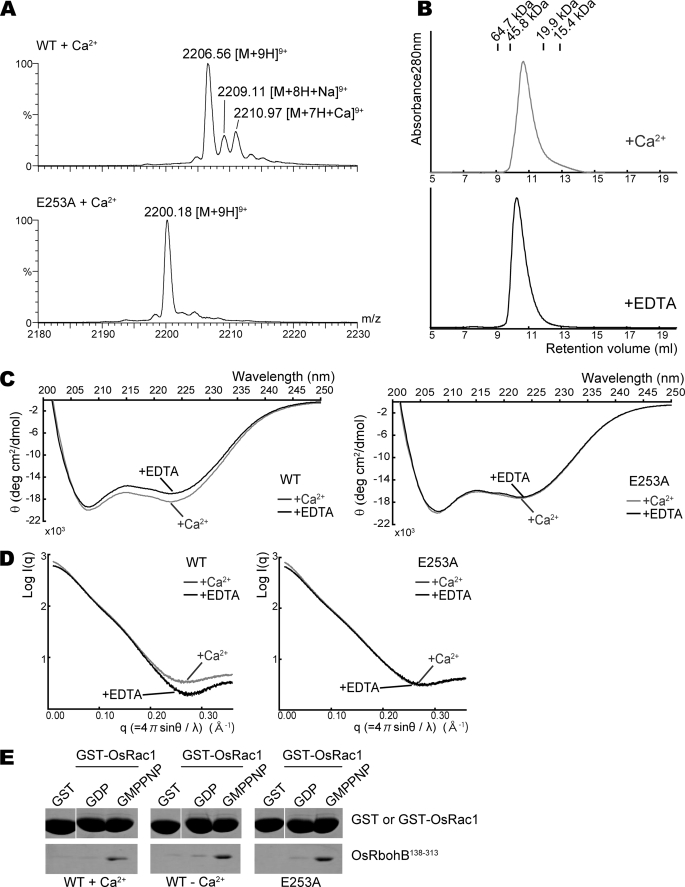
FIGURE 3.
Effects of Ca2+ binding on dimer formation and the conformation of OsRbohB-(138–313). A, expanded ESI mass spectra of wild-type OsRbohB-(138–313) and the E253A mutant. Stock solutions of both proteins were dialyzed against 500 mm ammonium acetate with 0.2 mm Ca(CH3COO)2; then, the dialyzed samples were diluted with 500 mm ammonium acetate to prepare solutions of 50 μm protein with 5.7 μm Ca2+. B, gel filtration chromatography profiles for Ca2+-bound and EDTA-treated OsRbohB-(138–313). Both are eluted at a similar position. C, CD spectra of the wild type (left) and E253A mutant (right) of OsRbohB-(138–313). Curves in gray and black show spectra determined in the presence of Ca2+ and EDTA, respectively. D, scattering curves of SAX in the wild type (left) and E253A mutant (right) of OsRbohB-(138–313). Curves in gray and black were determined in the presence of Ca2+ and EDTA, respectively. E, in vitro pulldown assays of GST-OsRac1 with the wild type or E253A mutant of OsRbohB-(138–313). OsRbohB-(138–313) was incubated with GST alone, or with the GDP-bound or the GMP-P(NH)P-bound forms of GST-OsRac1, in the presence or absence of Ca2+ (left and middle). The E253A mutant of OsRbohB-(138–313) was incubated with Ca2+ (right).