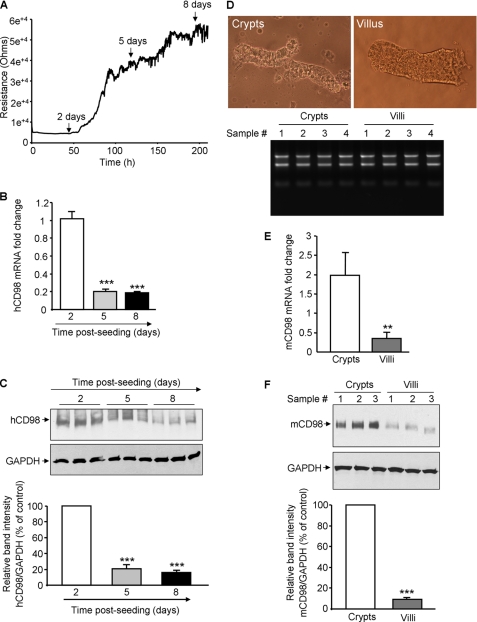
FIGURE 1.
Expression of CD98 is decreased during differentiation of intestinal epithelial cells. A–C, human (h) CD98 expression is decreased during Caco2-BBE cell differentiation. A, resistance of Caco2-BBE cells (2 × 104 cells/400 μl/electrode) was measured at 500 Hz, 1 V in real-time using the ECIS device. B and C, hCD98 expression levels in Caco2-BBE cells cultured on plastic plates for 2, 5, and 8 days were analyzed by real-time RT-PCR (B) and Western blot (C). Bar graphs in C show the relative intensity of blots in the upper panel. Values represent means ± S.E. of three determinations. *, p < 0.05; ***, p < 0.001; NS, not statistically significant versus day 2 (white bar). D–F, mouse (m) CD98 expression is decreased toward the crypt-villus axis of mouse intestine. D, villi and crypts were isolated from jejunum of 6–8-week-old FVB male mice. Pictures of the extracted villus and crypt fractions were taken using a Nikon Eclipse TS100 microscope at ×10 and ×40 magnifications, respectively (upper panels). Total RNAs from villi and crypts were extracted, and their integrity was shown (bottom panel). mCD98 expression levels in the villus and crypt fractions were assessed by real-time RT-PCR (E) and Western blot (F). Bar graphs in F show the relative intensity of blots in the upper panel. Values represent means ± S.E. of three determinations. **, p < 0.005; ***, p < 0.001.