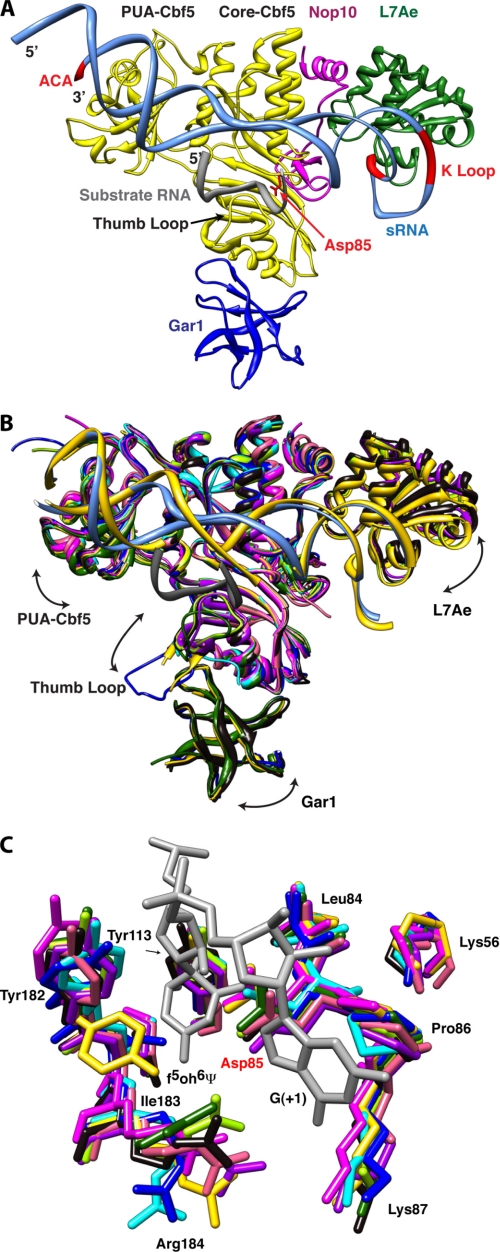
FIGURE 1.
Structural comparison of box H/ACA RNPs. A, overall structure of the box H/ACA RNP. The conserved ACA sequence and K-turn motif of the guide RNA and the catalytic aspartate residue of Cbf5 are shown in red. Substrate RNA (gray), guide RNA (aqua), Cbf5 (yellow), Gar1 (blue), L7Ae (green), and Nop10 (magenta) are shown. In this structure, the thumb loop is in its closed (or RNA-bound) conformation. B, structural comparison of box H/ACA RNP complexes and subcomplexes. Arrows indicate the directions of molecular motion suggested by variability between structures. Ribbon representations of the superimposed structures of the Cbf5-Nop10 complexes (pink, Protein Data Bank code 2APO (28); and salmon, code 2AUS (27)), the Cbf5-Gar1-Nop10 complex (green, code 2EY4 (26)), the Cbf5-Gar1-L7Ae-Nop10-guide RNA complex (yellow, code 2HVY (24)), the Cbf5-Nop10-guide RNA-substrate RNA complex (sky blue, code 3HJY (21)), the Cbf5-Gar1-Nop10-guide RNA-substrate RNA complex (blue, code 2RFK (25)), the Cbf5-L7Ae-Nop10-guide RNA-substrate RNA complex (light green, code 3HAX (20); and purple, code 3HJW (21)), and the full complex with substrate RNA (black, code 3HAY (20)) are shown. A single guide RNA from substrate-bound (aqua) and substrate-free (yellow) structures and the docked substrate RNA (gray) are shown. C, conserved active site residues of Cbf5. The color scheme is as described for B. Only two nucleotides from the substrate RNA, including the isomerized 5-fluorouridine (5-fluoro-6-hydroxypseudouridine (f5oh6Ψ)), are shown in gray. Structures were superimposed and displayed using UCSF Chimera (48, 49) employing the Cbf5-Nop10 complex (code 2APO (28)) as the reference.