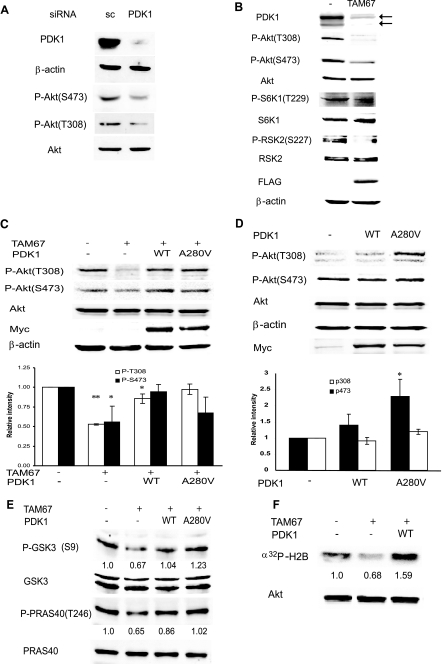
FIGURE 4.
c-Jun regulates Akt activity via PDK1. A, PDK1 is required for Akt phosphorylation and activation. Protein extracts (40 μg) from Lu1205 cells transfected with scrambled (sc) oligonucleotides or siRNA specific for PDK1 were analyzed by Western blots using the indicated antibodies. B, TAM67 inhibits constitutive phosphorylation of Akt, S6K1, and RSK2. Protein extracts from Lu1205 or Lu1205 cells stably transfected with FLAG-TAM67 were blotted with the indicated antibodies. C, c-Jun-dependent regulation of Akt activation is mediated by PDK1. Lu1205-FLAG-TAM67 cells were infected with retrovirus expressing either WT PDK1 or the constitutively active PDK1 mutant A280V, and stable lines expressing exogenous PDK1 were established. Both PDK1 proteins are Myc-tagged. Protein extracts (40 μg) were blotted with the indicated antibodies. The intensity of bands corresponding to Thr308 and Ser473 phosphorylation from three independent experiments was determined, normalized to levels of total Akt, and plotted. Results are shown as the mean ± S.D. **, represents p < 0.0005. *, represents p < 0.05. D, expression of exogenous PDK1 causes a minimal increase in Akt phosphorylation. Lu1205 cells, which harbor mutant Pten, were infected with retrovirus expressing either WT PDK1 or the constitutively active mutant A280V, and stable cell lines were established. Protein extracts were analyzed as indicated in panel C. * represents p < 0.05. E, c-Jun-dependent regulation of PDK1 affects phosphorylation of Akt substrates. Protein extracts from cells described in panel C were analyzed with the indicated antibodies. The intensity of bands corresponding to p-GSK3β (S9) and p-PRAS40 (T246) was determined and normalized to total GSK3 and PRAS40, respectively. The degree of phosphorylation in the first lane was set to 1. Similar results were obtained in three separate experiments. F, c-Jun-dependent regulation of PDK1 affects Akt kinase activity. Akt was immunoprecipitated from cells described in the legend for Fig. 3C, and an in vitro kinase assay was performed. The relative intensity of the phosphorylated substrate is indicated. Similar results were obtained in three separate experiments.