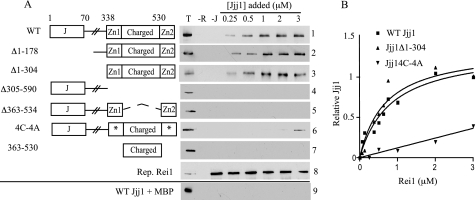
FIGURE 1.
Jjj1 interacts directly with Rei1. A, to assay Jjj1-Rei1 binding, maltose-binding protein-tagged Rei1 (MBP-Rei1) was prebound to amylose resin and then incubated with the indicated concentrations of WT Jjj1 (panel 1) or Jjj1 variants (panels 2–7). The J domain (J), zinc fingers (Zn1 and Zn2), and charged region, which are designated in the adjacent diagrams, are described more fully under “Results.” Asterisks indicate zinc finger 1 and 2 cysteine to alanine alterations. After pelleting of the resin, Jjj1 binding was assessed by immunoblotting using anti-Jjj1 antibody. Three control lanes were included in each panel: 0.25 μm of Jjj1 protein (T); resin with no Rei1 added (−R); and resin with no Jjj1 added (−J). In addition, a representative blot of MBP-Rei1 was incubated with MBP-specific antibody (panel 8), and MBP alone was prebound to resin and incubated with WT Jjj1 (panel 9). B, concentrations of MBP-Rei1 ranging from 0.06 to 3 μm were incubated with amylose resin prior to incubation with 1 μm WT Jjj1, Jjj1Δ1–304, or Jjj14C-4A. Bound Jjj1 was quantified by densitometry. The amount of WT Jjj1 pulled down by 3 μm Rei1 was set as 1. Values were plotted in GraphPad Prism using a single binding hyperbola to fit data obtained for WT Jjj1 and Jjj1Δ1–304 and linear regression to fit Jjj14C-4A.