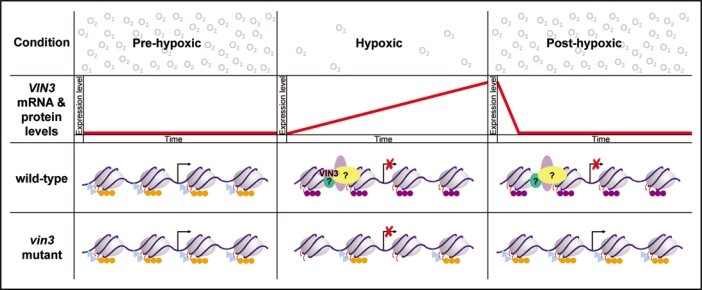
Figure 2.
One model for VIN3 action during low oxygen conditions; a comparison of wild-type and vin3 mutant plants. The proposed action of VIN3 during hypoxia is modelled on the action of VIN3 in the vernalization response where VIN3 is required for the repression of FLC expression during vernalization.1 VIN3 gene products (second row; red line) are not expressed under normal atmospheric oxygen levels (pre-hypoxic). Under these conditions VIN3 target genes are expressed in both wild-type plants (third row) and vin3 mutant plants (fourth row). The chromatin marks associated with actively transcribed genes are indicated: acetylated histone H3 and H4 (H3Ac and H4Ac; light blue triangles) and H3K4me3 (orange circles). Under hypoxic conditions the expression of some genes decreases in a VIN3 independent manner consistent with our gene expression microarray that did not identify genes that were differentially expressed in wild-type and vin3-4 mutant plants after 24 hours of hypoxia.11 In wild-type plants, where VIN3 expression is induced in a quantitative manner, VIN3 (pink) interacts with other chromatin remodelling proteins (green, purple and yellow) to set up a repressive chromatin state at VIN3 target genes. For example: the removal of H3Ac, H4Ac and H3K4me3 and the addition of repressive chromatin modifications, such as H3K27me3 (purple circles). The addition of H3K27me3 ensures that VIN3 target genes remain repressed on return to normal atmospheric conditions (post-hypoxic). Even though VIN3 is no longer present, the recruited chromatin remodelling complex maintains VIN3 target genes in a repressed state to promote the survival of Arabidopsis seedlings following prolonged hypoxia. In contrast to wild-type plants, the absence of VIN3 in a vin3 mutant would prevent the recruitment and formation of a chromatin remodelling complex at VIN3 target genes and thus there would be no addition of repressive chromatin modifications* to maintain VIN3 target genes in a repressed state post-hypoxia. *there maybe some removal of active modifications, as this could be performed by another chromatin remodelling complex.