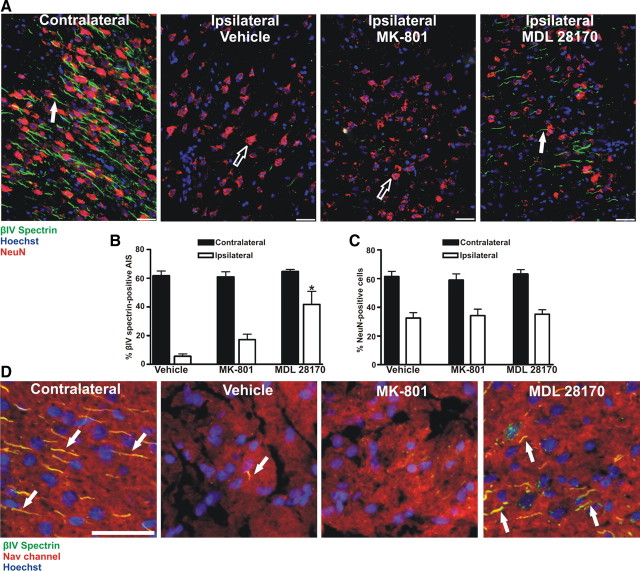
Figure 9.
Calpain inhibition in vivo attenuates AIS disassembly following ischemic injury. A, Rats were subjected to MCAO in the presence or absence (vehicle) of a cell-permeable calpain inhibitor (MDL 28170) or an NMDA antagonist (MK-801). Coronal sections of rat cortex were stained (t = 24 h post-occlusion) with the neuronal marker NeuN (red); the AIS was labeled with anti-βIV spectrin (green) and nuclei were labeled with Hoechst (blue). White arrows indicate βIV spectrin labeled AIS, while black arrows indicate NeuN labeled neurons. B, Quantification of the preservation of the AIS (n = 4 animals for each group). Compared to MK-801 or vehicle treated animals, AIS integrity is significantly increased (asterisk) in the infarcted region of the ipsilateral cortex (white bars) of MDL 28170-treated animals. C, Within the infarcted region of the ipsilateral cortex (white bars), NeuN staining is significantly reduced as compared to the contralateral cortices (black bars) in all treatment groups. D, Within infarcted regions, there was a significant increase in Nav channel/βIV spectrin-labeled (yellow; arrow) AIS in animals treated with the calpain inhibitor (MDL 28170) versus MK-801 or vehicle-treated animals. Scale bars: A, D, 50 μm.