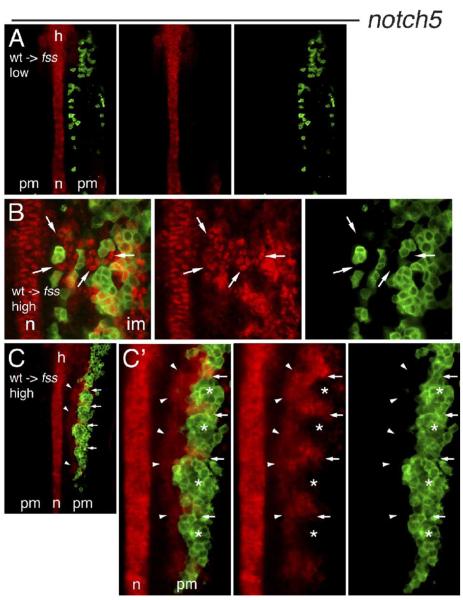
Fig. 4.
Induction of notch5 expression in fss/tbx24 host cells by wild-type neighbors. Expression of notch5 mRNA (red) in confocal sections of the PM of 5–6 somite stage fss/tbx24 host embryos containing transplanted cells (green) from wild-type donors. Embryos are flat mounted, anterior up. (A) notch5 is not expressed in the PM of fss/tbx24 host embryo with low density of wild-type donor cells. (B) High-magnification view of PM of fss/tbx24 host embryo containing high density of wild-type donor cells. Autonomous notch5 expression is seen in wild-type cells, and notch5 induction in numerous fss/tbx24 host cells (arrows) up to three cell diameters from the wild-type cell clones. (C) Periodic stripes of notch5 expression in fss/tbx24 host embryo containing 5 somite-like clusters of wild-type donor cells in the right-hand PM. Contralateral side does not express notch5. Arrows indicate the boundaries between clusters, arrowheads mark fss/tbx24 host PM cells expressing notch5.(C’) High magnification of the region of notch5 expression. Arrows and arrowheads as in panel C, asterisks mark the rostral half of cell clusters. Note high-level notch5 expression in the caudal part of each somite-like cluster. n = notochord, h = hindbrain, pm = paraxial mesoderm, im = intermediate mesoderm.