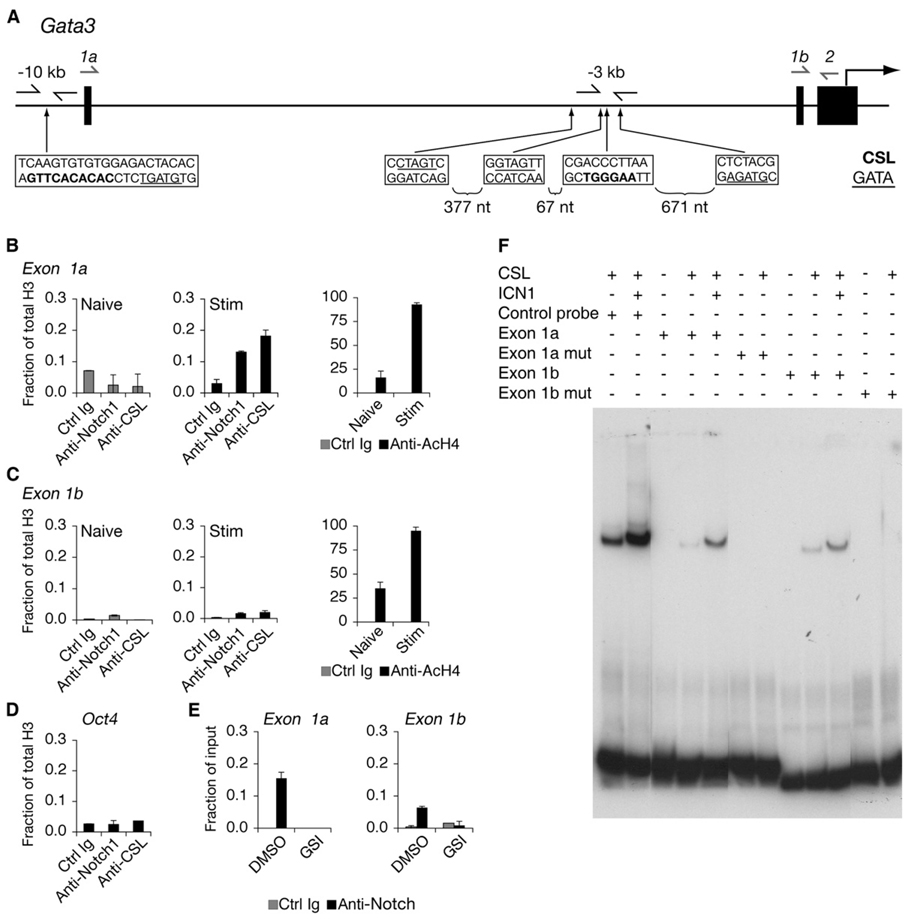
Figure 3. Notch Binds to Regions of Gata3 Containing CSL-Binding Sites.
(A) Schematic of the 5′ region of the Gata3 locus. Gata3 transcription can initiate from either exon 1a or exon 1b. The translational start site begins within exon 2. Locations of nucleotides matching the CSL-binding sites are shown in bolded sequences. GATA sites are underlined. Arrows immediately flanking these sites are primers used to amplify ChIP DNA. Arrows drawn above exon 1a or exon 1b were used as forward primers coupled with a reverse primer that annealed to exon 2 to amplify mRNA transcripts. The bottom strand in each box is indicated 5′ to 3′.
(B) Notch1 binds to the exon 1a CSL-binding site. Naive or CD4+ T cells stimulated for 40 hr were purified and fixed for ChIP. Antibodies used for IP are a control IgG, α-Notch1, α-CSL, α-acetylated H4 (AcH4), and α-H3. Total histone H3 was used for normalization. Graphs represent quantitative PCR presented as a mean of the ratios of the amount of IP DNA in each sample relative to total H3 from values of duplicate wells ±SD. Data are representative of at least three independent experiments.
(C) Notch1 binds weakly to the exon 1b CSL-binding site. The description is the same as (B), except the primers amplified the CSL-binding site upstream of exon 1b.
(D) ChIP from CD4+ T cells stimulated for 40 hr and quantitative PCR for an irrelevant gene control (Oct4). Data are representative of at least three independent experiments.
(E) GSI treatment blocks association of Notch1 with Gata3 CSL-binding sites. CD4+ T cells were treated with either DMSO (vehicle control) or GSI and stimulated for 40 hr, and ChIP was performed. Data are representative of three independent experiments.
(F) CSL binds to putative target sequences within the Gata3 locus. Wild-type or mutant oligonucleotides corresponding to exon 1a or exon 1b CSL-binding sites were labeled with 32P and mixed with buffer alone or buffer containing purified CSL or Notch1 polypeptides, or both, and electrophoresed. Gels were dried, and probes were detected by autoradiography. The control probe contained a consensus CSL-binding site.