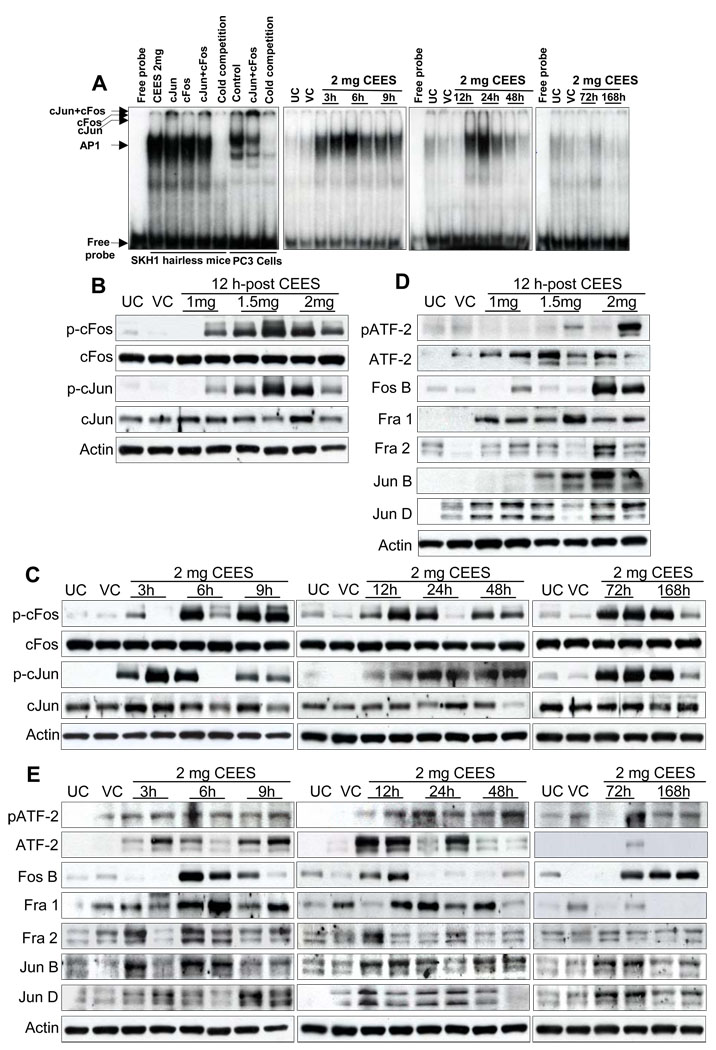
Fig. 7.
Effect of topical CEES exposure on activation of AP-1 family proteins in SKH-1 hairless mouse skin. Mice were treated topically with different doses of CEES or acetone alone, and the dorsal skin was collected at specific time points as detailed under Materials and Methods. Nuclear lysates were subjected to DNA binding activity by EMSA, for competition with cold AP1 consensus oligo, and super shift assay was conducted as described under Materials and Methods (A). Western blot analysis was done after 12 h treatment for phospho- and total cFos and cJun (B), and phospho- and total ATF-2, Fos B, Fra-1, Fra-2, Jun B, Jun D (D). These AP1 family proteins were similarly analyzed in time response study (C and E) employing 2 mg CEES as described under Materials and Methods. The membranes were stripped and reprobed with β-actin as loading control. The results are representative of two animals in each dose- and time-response study. UC, untreated control; VC, vehicle control.