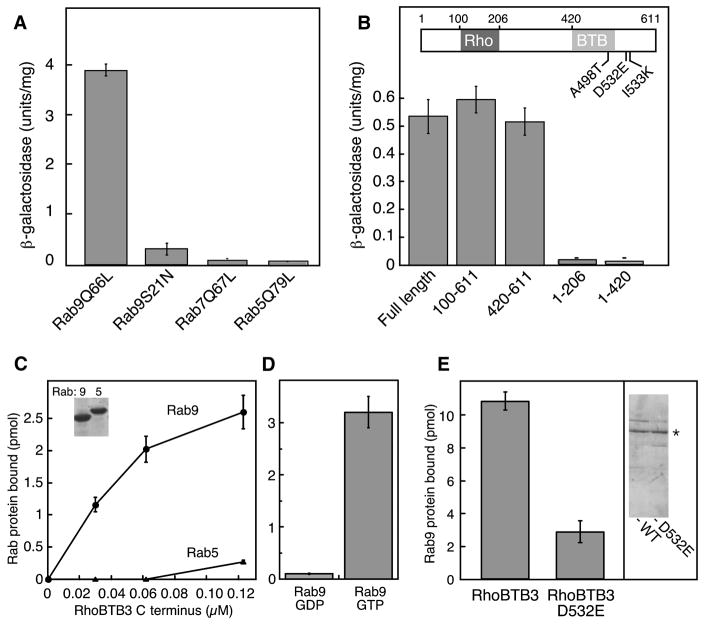
Figure 2. RhoBTB3 interacts specifically with Rab9 GTPase via its C-terminus.
(A) Liquid culture β-galactosidase activity of yeast strains coexpressing the clone 8-GAL4 activation domain (RhoBTB3 131–607) hybrid and GAL4-DNA binding domain hybrids of either Rab9Q66L, Rab9S21N, Rab7Q67L, or Rab5Q79L. (B) Liquid culture of β-galactosidase activity of yeast strains coexpressing the indicated RhoBTB3 fragments with the GAL4 DNA binding domain of Rab9Q66L. Error bars in A and B represent standard deviation of duplicate determinations from a representative experiment. RhoBTB3 C-terminus (420–607) was subjected to PCR-based mutagenesis and assayed for subsequent Rab9 binding by two hybrid screening; point mutations that abolished Rab9 binding are indicated. (C) (Left panel) Increasing amounts of purified GST-RhoBTB3 C-terminus (AA 420-611) were incubated with purified Rab9 or Rab5 (600nM), preloaded with 35S-GTPγS. Inset, SDS-PAGE of proteins used for these experiments. (D) GST-RhoBTB3 C-terminus (AA 420-611; 180nM) binding to Rab9 bearing either 35S-GTPγS- or 3H-GDP as in C. Error bars represent standard deviation. (E) Binding of full length wildtype or RhoBTB3 D532E proteins (100nM) to Rab9-GTP (3μM). Inset at right shows Coomassie stained SDS-PAGE of the proteins used. Asterisk indicates His-RhoBTB3 full length.