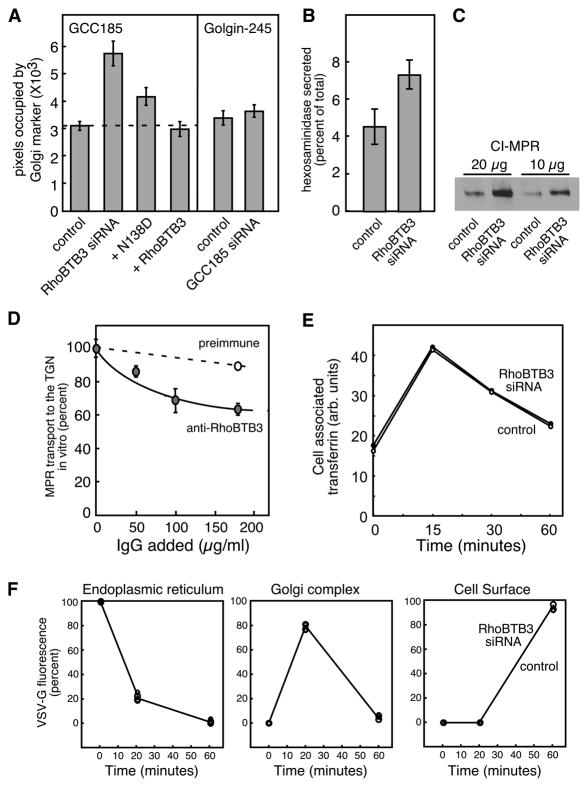
Figure 4. RhoBTB3 depletion expands the Golgi and blocks MPR trafficking.
(A) Quantitation of Golgi area. Left, GCC185 area in control cells (n=210), cells depleted of RhoBTB3 (n=44), or in cells expressing wild type RhoBTB3 (n=42) or N138D RhoBTB3 (n=60), was quantified using a Matlab script. Right, Golgi area in control cells (n=48) or in cells depleted of GCC185 (n=67) using Golgin245 staining. (B) Lysosomal enzyme secretion upon depletion of RhoBTB3. Cells were treated for 72 hours with siRNA against RhoBTB3 and assayed for secretion of hexosaminidase. Both control and depleted cells contained 5.2 × 103 units/mg hexosaminidase. (C) Immunoblot analysis of CI-MPR levels in control or RhoBTB3 depleted cell extracts; 10 or 20μg of HeLa extracts were analyzed as indicated. (D) MPR transport from endosomes to the TGN (Reddy et al., 2006) was carried out for 90 min. in the presence or absence of the indicated amounts of non-immune or rabbit anti-RhoBTB3 IgG. In A, error bars represent standard error of the mean; in B and D, standard deviation of duplicate samples from a representative experiment are shown. (E) Alexa-594-Transferrin (50μg/ml) was prebound to cells on ice for 60 minutes; cells were warmed for various times and cell-associated transferrin was determined after washing with 20mM HOAC pH3, 500mM NaCl by immunofluorescence and MatLab analysis in control and RhoBTB3 depleted HeLa cells (>50 cells counted for each time point in two separate experiments; average of both is shown). (F) YFP-VSV-G-ts045 transport through the ER, Golgi and cell surface was carried out as described (Sklan et al., 2007) for control and RhoBTB3 depleted cells, with >150 cells counted at each time point, in two separate experiments, one of which is shown. The two data sets were identical.