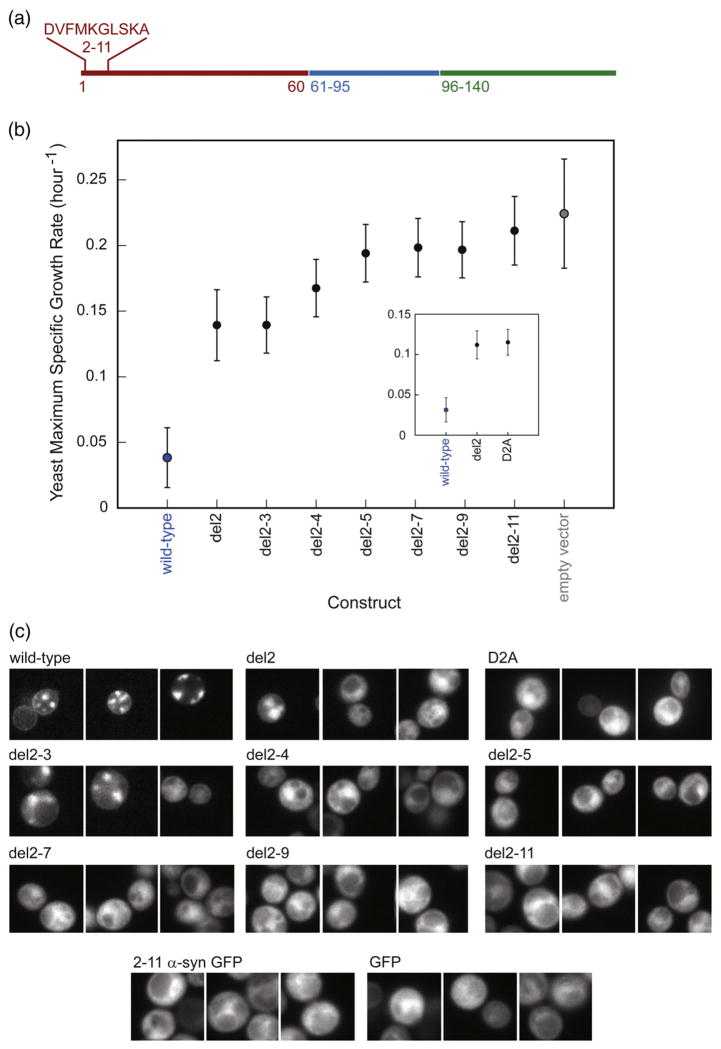
Fig. 5.
N-terminal deletions dramatically reduce yeast toxicity. (a) The location and identity of the deleted amino acids are shown in wild-type α-syn. (b) Yeast maximum specific growth rates of the variants, listed in order of increasing deletion size. The D2A mutant behaves like del2 (insert). (c) Microscopy of GFP-tagged N-terminally truncated α-syns. Deletion of Asp2 or D2A substitution reduces membrane localization and inclusion formation. Variants lacking three or more amino acids from the N-terminus localize to the cytoplasm. GFP bearing α-syn amino acids 2–11, unlike GFP-tagged α-syn, does not associate with the plasma membrane, suggesting that the N-terminal amino acids are not a membrane localization sequence.