Abstract
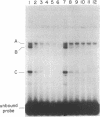
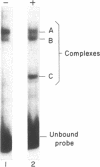
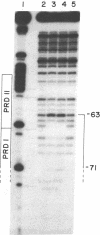
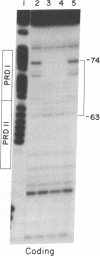
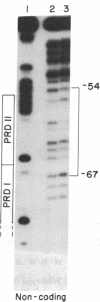
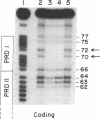
Human beta-interferon gene expression is induced by virus or poly(I).poly(C). This induction is due at least in part to an increase in the rate of transcription and does not require protein synthesis. A 40-base-pair DNA sequence within the beta-interferon promoter, termed the interferon gene regulatory element (IRE), is an inducible enhancer in mouse fibroblasts, and both positive and negative regulatory DNA sequences have been identified within this element. In this paper we identify three factors that bind specifically to two positive regulatory domains within the IRE. Two of these factors are present in nuclear extracts prepared from uninduced and induced cells; one is present only in extracts from induced cells. The functional significance of these binding activities was demonstrated by showing that point mutations within the IRE that decrease human beta-interferon gene transcription in vivo prevent binding in vitro. We propose that induction of the beta-interferon gene involves the modification of a protein to a form that binds specifically to a positive regulatory sequence within the IRE.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angel P., Imagawa M., Chiu R., Stein B., Imbra R. J., Rahmsdorf H. J., Jonat C., Herrlich P., Karin M. Phorbol ester-inducible genes contain a common cis element recognized by a TPA-modulated trans-acting factor. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90611-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavalieri R. L., Havell E. A., Vilcek J., Pestka S. Induction and decay of human fibroblast interferon mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4415–4419. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T., Ohno S., Yasumitsu H., Taniguchi T. Delimitation and properties of DNA sequences required for the regulated expression of human interferon-beta gene. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):489–496. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T., Shibuya H., Hotta H., Yamanishi K., Taniguchi T. Interferon-beta gene regulation: tandemly repeated sequences of a synthetic 6 bp oligomer function as a virus-inducible enhancer. Cell. 1987 May 8;49(3):357–367. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90288-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Revzin A. A gel electrophoresis method for quantifying the binding of proteins to specific DNA regions: application to components of the Escherichia coli lactose operon regulatory system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3047–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodbourn S., Burstein H., Maniatis T. The human beta-interferon gene enhancer is under negative control. Cell. 1986 May 23;45(4):601–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90292-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodbourn S., Maniatis T. Overlapping positive and negative regulatory domains of the human beta-interferon gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1447–1451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodbourn S., Zinn K., Maniatis T. Human beta-interferon gene expression is regulated by an inducible enhancer element. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):509–520. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80024-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lengyel P. Biochemistry of interferons and their actions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:251–282. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Goodbourn S., Fischer J. A. Regulation of inducible and tissue-specific gene expression. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1237–1245. doi: 10.1126/science.3296191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nir U., Cohen B., Chen L., Revel M. A human IFN-beta 1 gene deleted of promoter sequences upstream from the TATA box is controlled post-transcriptionally by dsRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):6979–6993. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.6979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prywes R., Roeder R. G. Inducible binding of a factor to the c-fos enhancer. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):777–784. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90520-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raj N. B., Pitha P. M. Two levels of regulation of beta-interferon gene expression in human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3923–3927. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehgal P. B., Dobberstein B., Tamm I. Interferon messenger RNA content of human fibroblasts during induction, shutoff, and superinduction of interferon production. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3409–3413. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Inducibility of kappa immunoglobulin enhancer-binding protein Nf-kappa B by a posttranslational mechanism. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):921–928. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90807-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorger P. K., Lewis M. J., Pelham H. R. Heat shock factor is regulated differently in yeast and HeLa cells. Nature. 1987 Sep 3;329(6134):81–84. doi: 10.1038/329081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staudt L. M., Singh H., Sen R., Wirth T., Sharp P. A., Baltimore D. A lymphoid-specific protein binding to the octamer motif of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Oct 16;323(6089):640–643. doi: 10.1038/323640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss F., Varshavsky A. A protein binds to a satellite DNA repeat at three specific sites that would be brought into mutual proximity by DNA folding in the nucleosome. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):889–901. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90424-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Topol J., Ruden D. M., Parker C. S. Sequences required for in vitro transcriptional activation of a Drosophila hsp 70 gene. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):527–537. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90110-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimarino V., Wu C. Induction of sequence-specific binding of Drosophila heat shock activator protein without protein synthesis. 1987 Jun 25-Jul 1Nature. 327(6124):727–730. doi: 10.1038/327727a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinn K., DiMaio D., Maniatis T. Identification of two distinct regulatory regions adjacent to the human beta-interferon gene. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):865–879. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90544-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinn K., Maniatis T. Detection of factors that interact with the human beta-interferon regulatory region in vivo by DNAase I footprinting. Cell. 1986 May 23;45(4):611–618. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90293-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]