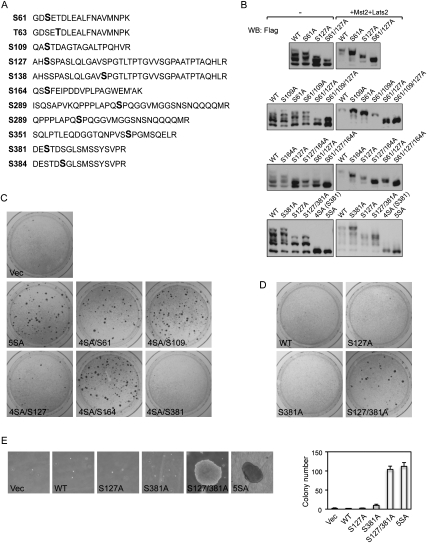
Figure 1.
Phosphorylation of S127 and S381 inhibits YAP oncogenic activity. (A) YAP is phosphorylated in vivo on all five Lats phosphorylation consensus sites (S61, S109, S127, S164, and S381). YAP expressed in MCF10A cells was tandem affinity-purified and analyzed by LC-MS/MS. Identified YAP phosphopeptides were shown. Phosphorylated residues are highlighted in bold. (M′) Methionine oxidation. In the phosphopeptide containing S163 and S164, the mass spectronomy data could not determine which one of them is phosphorylated. However, S164 phosphorylation was confirmed by later experiments and therefore is highlighted here. (B) Mutations of S61, S109, S127, and S164 to alanine increase YAP electrophoretic mobility. YAP wild type and mutants were expressed in HEK293 cells with or without Mst and Lats cotransfection as indicated. Cell lysates were resolved on SDS-PAGE gels containing 25 mM Phos tag-conjugated acrylamide followed by standard Western blotting with anti-Flag antibody. (C) Restoration of Ser 127 or Ser 381 is sufficient to inhibit YAP-5SA transformation activity. NIH-3T3 cell colony formation assays were performed using vector control or indicated YAP constructs. Colonies were visualized with crystal violet staining 2 wk after transfection. Expression of YAP wild type or mutants 24 h after transfection was shown by Western blot (Supplemental Fig. S1B). (D) Mutation of both Ser 127 and Ser 381 is required to activate YAP transforming activity. Experiments were similar to those in C with indicated YAP constructs. Expression of YAP wild type or mutants 24 h after transfection was shown by Western blot (Supplemental Fig. S1C). (E) Transformation of MCF10A cells by YAP-S127/381A and YAP-5SA. Indicated MCF10A stable cells were cultured in soft agar for 16 d before pictures were taken. Colonies were then visualized by crystal violet staining and colonies observable by the naked eye were counted and are shown in the right panel.