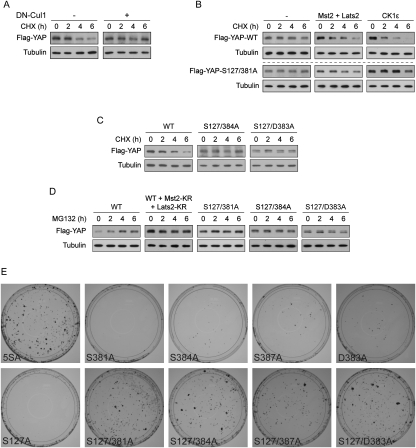
Figure 7.
Inhibition of YAP oncogenic transformation ability through SCFβ-TRCP-mediated YAP degradation depends on the Hippo pathway, CK1δ/ɛ, and the phosphodegron. (A) YAP degradation is inhibited by dominant-negative Cul1. Flag-YAP was transfected into NIH-3T3 cells at low expression level alone (left panels) or together with dominant-negative Cul1 (right panels), and cells were cultured to confluence. Cells were treated with 50 μg/mL CHX for the indicated time. Anti-Flag Western blot was used to show YAP protein levels and anti-tubulin Western blot was used as a loading control. (B) The Hippo pathway and CK1ɛ destabilize YAP in a S381-dependent manner. Flag-YAP wild type or S127/381A mutant were transfected alone or together with the Hippo pathway components Mst2/Lats2, or CK1ɛ into NIH-3T3 cells. Cells were cultured at low density so that most cells do not have contact with each other. CHX chase and Western blots were done as in A. (C) Mutation of S384 or D383 in the phosphodegron stabilizes YAP. YAP wild type or mutants were transfected into NIH-3T3 cells. Cells were cultured to confluence, and CHX chase and Western blots were done as in A. (D). Regulation of YAP stability by proteasome is dependent on functional Hippo pathway, as well as S381 and the phosphodegron of YAP. Flag-YAP wild type or mutants were transfected alone or together with kinase-inactive Mst2-KR and Lats2-KR as indicated. Cells were cultured to confluence and were treated with 25 μM MG132 for the indicated time before harvest. Western blots were done as in A. (E) Mutation of the phosphodegron together with S127 is sufficient for YAP to transform NIH-3T3 cells. NIH-3T3 cell colony formation assays were performed using indicated YAP constructs. Colonies were visualized with crystal violet staining.